Table of Contents
Uncertainty in Machine Learning: Probability & Noise
Image by Author
Editor’s note: This article is a part of our series on visualizing the foundations of machine learning.
Welcome to the latest entry in our series on visualizing the foundations of machine learning. In this series, we will aim to break down important and often complex technical concepts into intuitive, visual guides to help you master the core principles of the field. This entry focuses on the uncertainty, probability, and noise in machine learning.
Uncertainty in Machine Learning
Uncertainty is an unavoidable part of machine learning, arising whenever models attempt to make predictions about the real world. At its core, uncertainty reflects a lack of complete knowledge about an outcome and is most often quantified using probability. Rather than being a flaw, uncertainty is something models must explicitly account for in order to produce reliable and trustworthy predictions.
A useful way to think about uncertainty is through the lens of probability and the unknown. Much like flipping a fair coin, where the outcome is uncertain even though the probabilities are well defined, machine learning models frequently operate in environments where multiple outcomes are possible. As data flows through a model, predictions branch into different paths, influenced by randomness, incomplete information, and variability in the data itself.
The goal of working with uncertainty is not to eliminate it, but to measure and manage it. This involves understanding several key components:
- Probability provides a mathematical framework for expressing how likely an event is to occur
- Noise represents irrelevant or random variation in data that obscures the true signal and can be either random or systematic
Together, these factors shape the uncertainty present in a model’s predictions.
Not all uncertainty is the same. Aleatoric uncertainty stems from inherent randomness in the data and cannot be reduced, even with more information. Epistemic uncertainty, on the other hand, arises from a lack of knowledge about the model or data-generating process and can often be reduced by collecting more data or improving the model. Distinguishing between these two types is essential for interpreting model behavior and deciding how to improve performance.
To manage uncertainty, machine learning practitioners rely on several strategies. Probabilistic models output full probability distributions rather than single point estimates, making uncertainty explicit. Ensemble methods combine predictions from multiple models to reduce variance and better estimate uncertainty. Data cleaning and validation further improve reliability by reducing noise and correcting errors before training.
Uncertainty is inherent in real-world data and machine learning systems. By recognizing its sources and incorporating it directly into modeling and decision-making, practitioners can build models that are not only more accurate, but also more robust, transparent, and trustworthy.
The visualizer below provides a concise summary of this information for quick reference. You can find a PDF of the infographic in high resolution here.
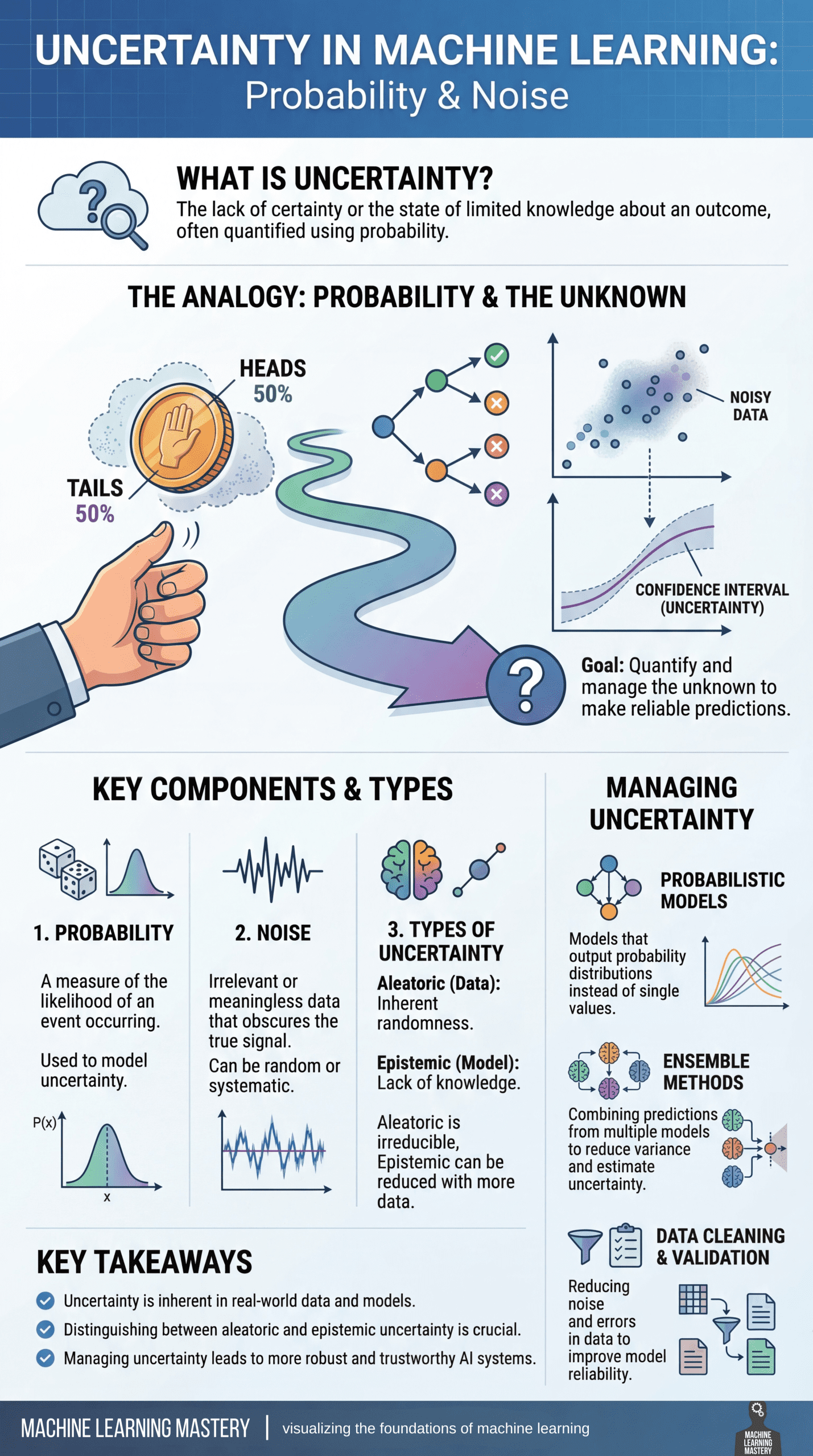
Uncertainty, Probability & Noise: Visualizing the Foundations of Machine Learning (click to enlarge)
Image by Author
Machine Learning Mastery Resources
These are some selected resources for learning more about probability and noise:
- A Gentle Introduction to Uncertainty in Machine Learning – This article explains what uncertainty means in machine learning, explores the main causes such as noise in data, incomplete coverage, and imperfect models, and describes how probability provides the tools to quantify and manage that uncertainty.
Key takeaway: Probability is essential for understanding and managing uncertainty in predictive modeling. - Probability for Machine Learning (7-Day Mini-Course) – This structured crash course guides readers through the key probability concepts needed in machine learning, from basic probability types and distributions to Naive Bayes and entropy, with practical lessons designed to build confidence applying these ideas in Python.
Key takeaway: Building a solid foundation in probability enhances your ability to apply and interpret machine learning models. - Understanding Probability Distributions for Machine Learning with Python – This tutorial introduces important probability distributions used in machine learning, shows how they apply to tasks like modeling residuals and classification, and provides Python examples to help practitioners understand and use them effectively.
Key takeaway: Mastering probability distributions helps you model uncertainty and choose appropriate statistical tools throughout the machine learning workflow.
Be on the lookout for for additional entries in our series on visualizing the foundations of machine learning.