Medical Invention and Discoveries
They say each new invention creates or brings solution to at least 10 problems. Discover the most recent Medical Discoveries of the past 3 years.
Top 5 Medical Discoveries and Invention in the past 3 years
A medical student in Canada has invented a cream that will erase tattoos. The cream, lipid-based, is almost transparent; once applied on the skin it penetrates the cells containing the pigment without causing any irritation or pain. Currently, tests are performed on tattooed mice.
Although tattoos tend to fade over time, it can take several decades to do so. Until now, the options available, laser and surgery, are painful, expensive and could leave marks. But using cream to remove tattoos is a new much simpler and painless technique that could revolutionize the process.
As for now, the researcher receives inquiries worldwide from people asking when the product will be available. If the cream successful remove tattoos, it would bring relief in the life of many people who get stuck with a tattoo on their skin which they no longer want.
Protein that rejects the AIDS virus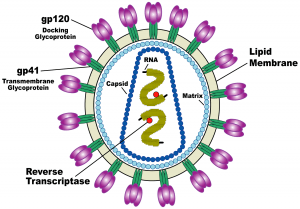
A team of researchers from The Scripps Research Institute, California, has discovered a protein capable of imitating human antibodies. This therapeutic protein has been found in coral waters of the coast of northern Australia.
This anti-HIV protein, cnidarian, was discovered from thousands of samples of natural products studied in the organic bank of the National Cancer Institute. Cnidarian proteins would be able to block the virus by preventing it from entering the T lymphocytes (T cells) responsible for cellular immunity.
“We found that cnidarins bind to the virus and prevent it from fusing with the T-cell membrane…This is completely different from what we’ve seen with other proteins, so we think the cnidarin proteins have a unique mechanism of action”, said Dr. Barry R. O’Keefe, an expert in the screening of natural product extracts and the discovery of novel bioactive compounds.
During the research, a group of monkeys that had been injected with the anti-HIV protein rejected the HIV, and thus avoid the contamination.
This is indeed an amazing discovery in the fight against HIV/AIDS when consider about 35.3 million people living with HIV worldwide. More than one million people die every year due to AIDS. The figures are alarming; and, so far, there is no sign of cure. This disease is a real global public health problem.
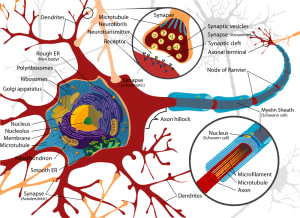 Human Brain connected to the immune system
Human Brain connected to the immune system
This is one of the most interesting of the recent medical discoveries. Scientists discovered the presence of lymphatic vessels in the brain. This is a major step towards a better understanding of neurodegenerative diseases.
Researchers at the University of Virginia would have detected the presence of lymph vessels in the brain of rodents. Before this discovery it was believed that the brain did not have direct anatomical relationship with the immune system. But as of 2015 this belief is thing of the past; the brain is in direct communication with the immune cells.
This system has many functions, including principally the movement of immune cells throughout the body and activation of the immune response during pathogenic attacks such as infection and cancer. It also contributes to the movements of hormones and assimilation of nutrients, and allows drainage of excess fluid in the tissues. All of these amazing functions are under control of the brain.
It’s just incredible. The presence of lymph vessels had thus escaped all the dissections performed until this discovery. And this is evidence show it is still possible to discover major anatomical structures in human body.
A group of researchers at Wisconsin-Madison University have managed to cultivate in laboratory folds of tissue similar to those of the vocal cords. They even managed to demonstrate their functionality. Not long ago culture of human living organs in the lab was an objective; now it is a reality.
The vocal cords constitute a set of complex tissue very difficult to imitate. They come in the form of folds located in the mucous membranes of the larynx. These folds are able to vibrate several hundred times per second to the passage of air to produce sound. Amazingly the scientists managed to reproduce them in lab.
The researchers also succeeded in transplanting the tissue into dead dogs and test their potential vibration by blowing humidified air over the coils. Against all odds, they managed to produce sounds with the same characteristics as the barking of a dog.
This invention will greatly help people who lose their vocal cords due to accident or drastic surgery such as surgical cancer treatment involving the removal of the membranous vocal fold (cordectomy).
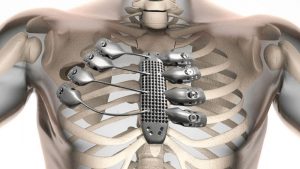
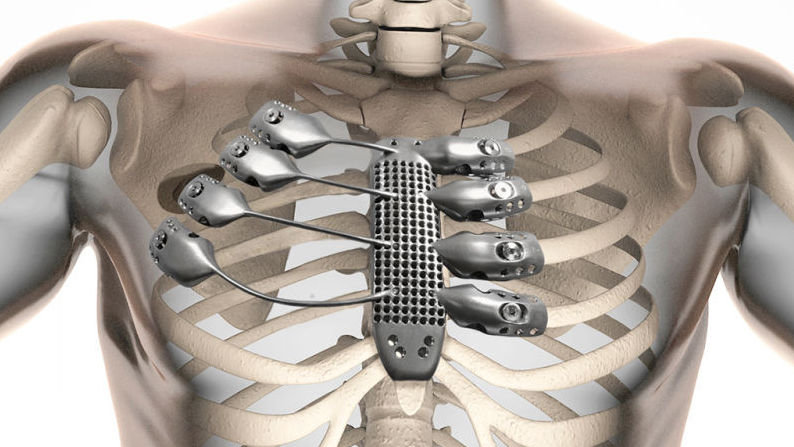
A 54 year-old Spaniard with a rare cancer of the chest had undergone removal of a section of his sternum last September. Through 3D printing, medical professionals designed a titanium sternum and ribs.
The patient was able to return home, and his recovery has been smooth. This is the first time this procedure has ever been performed.
The implant was manufactured by CSIRO 3D Printing, Lab 22. As one member of the production team, Alex Kingsbury says “The printer works by directing a beam of electrons to titanium powder in order to melt it. This process is then repeated to build the product layer by layer until they scientists have a complete implant. “
Once the implant is ready, it was sent to Spain and implanted in the patient who had his sternum and part of the chest removed. The operation was a success. 3D printing technology has created a body part which helps the 54 year old cancer survivor to live a normal life.

A group of British medical specialists grafted a functional bionic penis for a man, Mohammed Abad, who lost his penis and testes due to a car accident when he was six years old. The patient became the first man in the world to wear a bionic penis.
Since the age of six, Mohammed Abad, living in Edinburgh, Scotland, had no penis. But he was determined to have one. After a hundred surgeries the patient, now 44, has a functional sexual organ.
To recreate from scratch the penis skin was first levied on the left forearm of Mohammed. The internal functions of the organ are performed by a hand pump system located in the testes, which provides an erection within seconds. The bionic penis of about twenty centimeters realized through the work of surgeons at the University College London.
The Penis is Too Big for His wife
He hopes his new organ of pleasure would help him find the woman of his life and start a family. Indeed, he found a new woman. But there is a problem; “the penis is too big for me”, she complains.
Mohammad Abad had to undergo another surgical intervention to make the “instrument” smaller. After his girlfriend, Charlotte Rose, kept complaining sex was too painful due to the size of the penis, eight-inch. Is 8 inches really too big?
Muscle, Alive and Functional, Created in Laboratory
A group of researchers from Duke University in the US have managed to recreate a human muscle tissue with functional nerves, able to respond to external stimuli. This is a first in the history of bioengineering
This discovery represents an incredible opportunity for medical research. Scientists have finally recreated a muscle that does not just look like a human muscle but also works the same way.
This achievement opens of doors for many other medical adventures, especially on testing different drugs in development. It should therefore be possible to quickly conduct a battery of tests on these muscle cells without using human guinea pig for testing strong drugs.
To successfully recreate the muscle tissue in the lab, the American University research team has taken several cells by biopsy, extended and then placed them in a container filled with nourishing gel, acting somewhat like a 3D scaffold. It took nearly a year for the scientists to find the right size pan for their muscle.
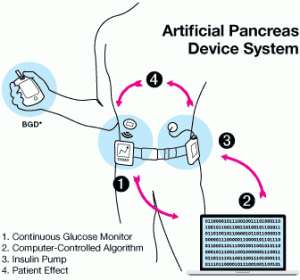
Some scientists created an artificial pancreas, which is still at the experimental stage, that delivers insulin in the blood as needed.
Different artificial pancreases are currently being tested in people suffering from type 1 diabetes to overcome the lack of insulin. The goal is to help patients to live a life free of constant injections of this valuable hormone that regulates sugar levels in the blood, and allows glucose to enter cells and be stored in the liver.
Currently, most patients have to make several injections a day. The lucky ones are equipped with an insulin pump, implantable or wearable. In the future, they will be increasingly likely to benefit from an artificial pancreas is in any case that the current experiments reveal to be successful.
It is, however, important to understand the artificial pancreas is not an organ built from scratch and put in the place of the real pancreas, such as an artificial heart which can fully replace the heart pump/muscle.
This is not a prosthetic organ to be implanted in the patient, but of an external technology, intended to compensate the loss of insulin secretion caused by the failing pancreas. The device consists of three key components: a sensor, a pump and an algorithm. Subcutaneous sensor measures the patient’s blood glucose continuously. The pump infuses insulin continuously via a thin nozzle positioned under the skin.