Alcoholism is a dependency on alcohol consumption and all pathological symptoms that it results. Alcoholism may also refer to pathological consequences of a prolonged and excessive alcohol abuse. The individual becomes physically dependent on alcohol to feel good (addiction).
Alcohol incidence is a major public concern in industrial countries; it is responsible for nearly 100,000 deaths each year. In developed countries like USA, alcohol is the third leading cause of death after cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Despite efforts of many organizations against alcohol abuse, the number of alcoholism increases daily. According to National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), “46.6 percent of people aged 12 or older reported drinking in the past 30 days”.
What are the causes of alcoholism?
Though the causes of alcoholism are not well known, scientists believe that the development of alcoholism depends on both psychological and socio-cultural factors.
Socio-cultural – People who live among drinkers or in an environment where it is easy to get alcohol are more apt to become alcoholism than those who live an alcohol-free environmental. The media contributes to the increase of alcohol dependence and abuse. Through TV advertising and appealing images, Alcohol companies play a major role in alcohol consumption. With that “cool portrait” alcohol is being attributed on television and the facility to obtain it, alcohol becomes a daily temptation to young adults.
apt to become alcoholism than those who live an alcohol-free environmental. The media contributes to the increase of alcohol dependence and abuse. Through TV advertising and appealing images, Alcohol companies play a major role in alcohol consumption. With that “cool portrait” alcohol is being attributed on television and the facility to obtain it, alcohol becomes a daily temptation to young adults.
Psychological – It is also shown that those who suffer from depression, anxiety and have low self-esteem are more apt to become alcoholic than those with a strong personality are.
Genetic and family conflicts are not excluded from the causes of alcoholism. Through the years, scientists have conducted many psychoanalytically, genetically and sociologically researches on family and personality of alcoholics. They have found that most young alcoholics are from absentee, abusive or alcoholic fathers, and/or mothers that are tyrannical and overprotective at the same time, which makes the children become insecure and aggressive.
In women, alcoholism occurs often in a context of narcissistic frustration, familial dissatisfaction, divorce, retrenchment situation. Socially mistreated, some women develop a secretive and solitary character. To have relief from their dissatisfaction, they embrace alcohol as a remedy to their problem. In addition, some neuroses, especially phobic, can also be a factor of alcoholism in women.
Common Signs of Alcoholism
At the beginning, alcoholism is asymptomatic (present no symptoms) for most people. Some may present abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, secretive behavior to hide alcohol use (mostly women).
If the alcohol dependence is not remediated, alcohol becomes a crucial part of the alcoholic. Symptoms of confusion, memory lapse, negligence (neglecting to eat and taking care of own personal hygiene and appearance), shaking in the morning, numbness and tingling, irregular pulse, dilation of capillaries, unstable approach, change of personality (uncontrolled anger, and unreasonable irritability, jealousy). In some people, occurrence of other alcohol-related illnesses may develop: gastrointestinal inflammation and irritation, acute or chronic pancreatic problems, low blood sugar, high blood fat content, infertility, bone fragility.
After years of heavy use of alcohol (usually 4 to 6 years), the dependency becomes an addiction; the victim needs regular use of alcohol to function. As the addiction aggravates, the alcoholic presents serious mental and physical deterioration, overall state of mental disorders. At this stage, not only the previous symptoms, but also the alcoholic becomes:
- Unable to stop or reduce alcohol intake;
- Hostile and violent toward those who try to help.
Alcohol Abuse Effects
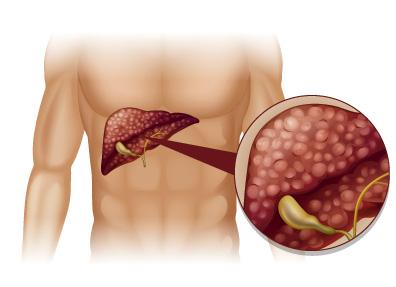 Physically and mentally, regular use of alcohol has no benefits. Heavy users of alcohol are exposed to a variety of diseases: sensitivity to bacterial infections (due to weakened immune system), bronchitis, liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis alcoholic), encephalopathy, and cancer of the oropharynx, esophagus, colon, liver, etc. Mentally, chronic alcoholism can lead to delirium tremens symptoms: fever, tachycardia, hypertension, intense hallucinations visions of insects, snakes or rats, tiny figures, etc.).
Physically and mentally, regular use of alcohol has no benefits. Heavy users of alcohol are exposed to a variety of diseases: sensitivity to bacterial infections (due to weakened immune system), bronchitis, liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis alcoholic), encephalopathy, and cancer of the oropharynx, esophagus, colon, liver, etc. Mentally, chronic alcoholism can lead to delirium tremens symptoms: fever, tachycardia, hypertension, intense hallucinations visions of insects, snakes or rats, tiny figures, etc.).
All those symptoms vary from one person to another; however, in women, effects of alcoholism are more serious and occur sooner than in men.
Diagnosis
An interrogation is always included in the diagnosis of alcoholism. Your doctor will assess whether you control your consumption of alcohol or if alcohol is controlling your life. This dialogue helps the physician to distinguish between regular consumption and casual consumption of alcohol. You may be asked questions about your personal, social and family history to detect if you:
- Drink in secret
- Hide bottles of alcohol at home or at work
- Impotence or lack of sexual desire
- Drink alcohol in the morning to feel better during the day
- Drink during social activities (work, important meeting, etc.)
- Lose interest in activities and entertainment that you once enjoyed
- Become angry when you are told to stop or control your alcohol consumption
- Consume alcohol even risking your life and that of others (drink while driving for example).
In addition, physical exam or clinical examination is often performed to confirm the diagnosis. Although they may be the signs of other medical conditions, the diagnosis is also aimed at discovering the following signs and symptoms:
- Sleep disorders
- Headache
- Digestive disorders or stomach problems
- Lack of concentration or memory problems
- Family issues (physical abuse, divorce, marital dispute, etc.)
- Skin problems (puffy face, skin discoloration)
- Nerve problems (tremors, loss of balance)
- Endocrinal problems (bilateral gynecomastia, Parotid gland inflammation)
Alcoholism Treatment
 Alcohol abuse treatment requires a complete motivation of the alcoholic to quit; otherwise, all efforts of doctors, family and friends would be vain. It implies a change of diet, from poor to a well-balanced healthy diet. In some cases, hospitalization is also required. For chronic alcoholics, certain psychiatrists use drugs (tranquilizers, antidepressants). Along with the treatment, some supplement and vitamins (niacin, vitamins D, vitamin K, folic acid, vitamin C, Vitamins B1, B2, B6, and B12,) are also helpful.
Alcohol abuse treatment requires a complete motivation of the alcoholic to quit; otherwise, all efforts of doctors, family and friends would be vain. It implies a change of diet, from poor to a well-balanced healthy diet. In some cases, hospitalization is also required. For chronic alcoholics, certain psychiatrists use drugs (tranquilizers, antidepressants). Along with the treatment, some supplement and vitamins (niacin, vitamins D, vitamin K, folic acid, vitamin C, Vitamins B1, B2, B6, and B12,) are also helpful.
Detoxification – Alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be severe. It is very important to follow a complete program of detoxification before beginning a treatment for alcoholism. The detoxification helps your body gets rid of certain effects of the alcohol and prepares it for drug treatments. In general, the detoxification program lasts one week or less.
Drug treatments – Certain alcohol-sensitizing drugs such as Disulfiram, Naltrexone and Campral (acamprosate calcium) are used in the alcohol abuse treatment in order to reduce the appetite for the stimulant; however, they may cause side effects which can be more severe than the effects of the alcohol



