Table of Contents
During defecation, the veins of your region recto-anal swell slightly to allow the elimination, that’s normal. The inflammation becomes a problem when it is recurring or permanent; this medical condition is called hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, refer to any medical condition causing abnormal dilation and inflammation of the veins of your lower rectum and anus.
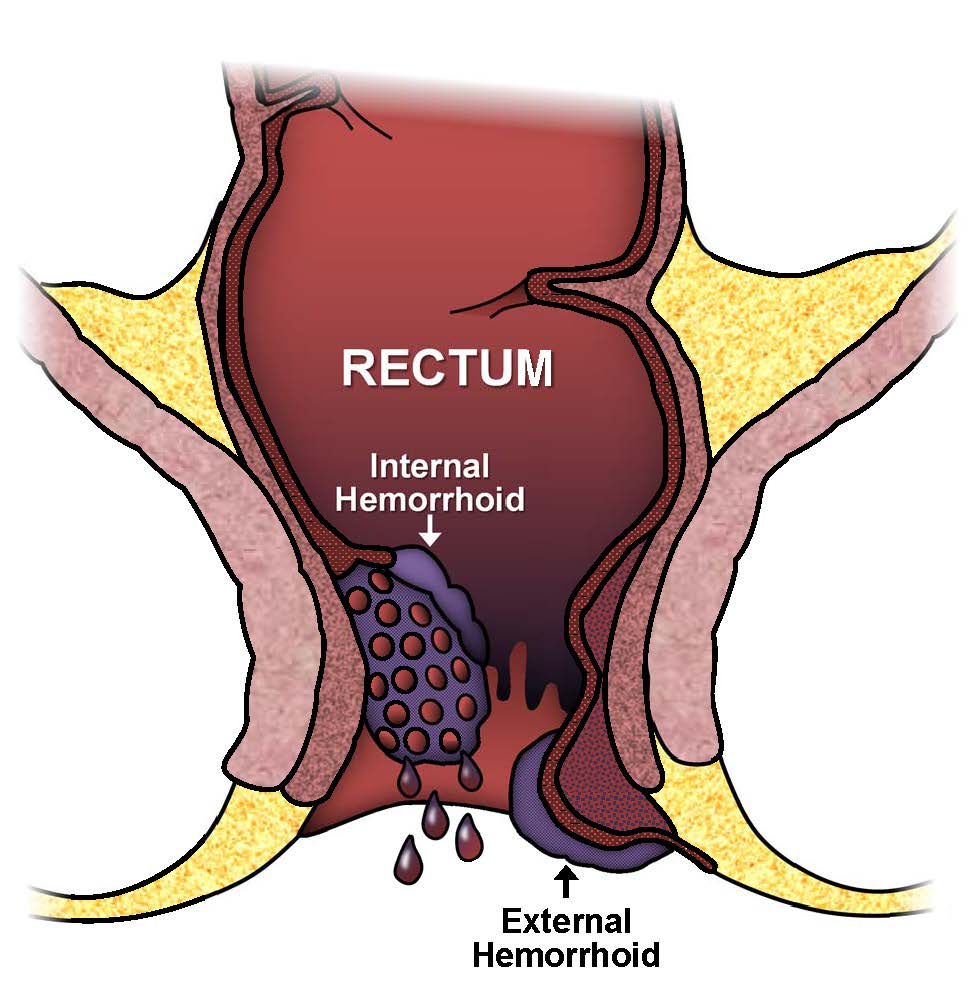
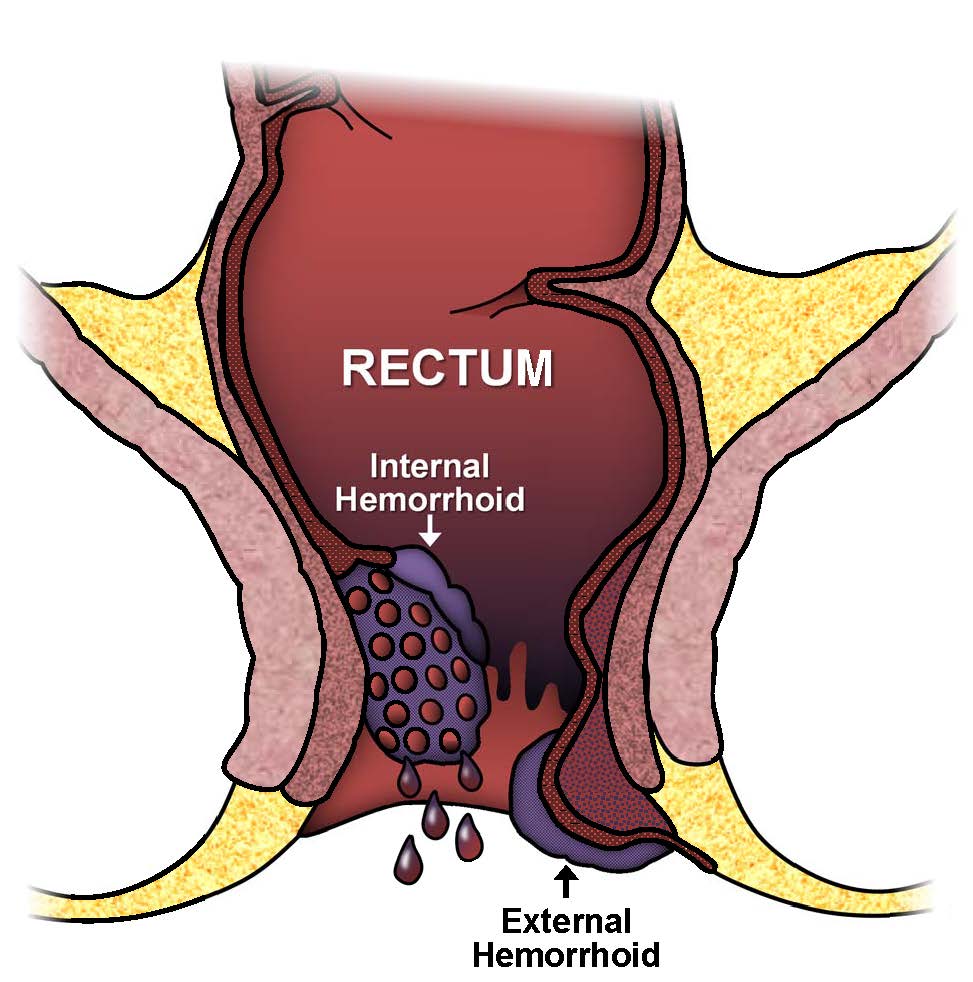
Depending on where it occurs, hemorrhoids can be external, prolapsed or internal.
External hemorrhoid is an itchy swelling disorder that occurs in the veins outside your anorectal junction. Sometimes, there is formation of blood clot in the dilated vein.
Internal hemorrhoid – Unlike external hemorrhoids, internal hemorrhoid involves the veins inside your lower rectum, and cause less pain. Sometimes, you can have feeling that your rectum is full. Although there is less or no pain, internal hemorrhoid can also cause itching or bleeding.
Prolapsed hemorrhoid – this condition occurs when internal hemorrhoid expand to the point of exit through your anus. Like external and internl, prolapsed hemorrhoid can be painful, itchy and hemorrhagic.
Hemorrhoids Causes and Risk Factors
All factors that increase pressure in the veins of your anus or rectum can lead to the development of hemorrhoids:
- Obesity
- Increased straining due to constipation or diarrhea
- Age (one in two people beyond 50 years diagnosed with hemorrhoids)
- Anal intercourse
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Heavy weight lifting
- Standing or sitting for long period of time
- Family history of hemorrhoids
- Excessive consumption of alcohol or caffeine
Hemorrhoids Symptoms and Warning Signs
Most common symptoms of Hemorrhoids include:
- Sensation of burning, itching during defecation
- Discomfort when you are sitting
- Presence of protrusions in your anus (external hemorrhoids)
- Inflammation and swelling inside or outside your anus
- Anal bleeding during defecation
- Hard lump around your anus due to formation of blood clot (thrombus)
- Mucus drainage caused mostly by infection or excessive use of toilet tissue.
Hemorrhoids Diagnosis
 In most cases, physical exam is enough to confirm external hemorrhoids. Diagnosis of internal hemorrhoids can require digital rectal examination (DRE), anuscopy and colonoscopy.
In most cases, physical exam is enough to confirm external hemorrhoids. Diagnosis of internal hemorrhoids can require digital rectal examination (DRE), anuscopy and colonoscopy.
Digital rectal examination – digital rectal examination is a part of the proctology examination, in which your doctor or nurse introduced a lubricated and gloved finger into your rectum through your anus. This exam allows your doctor to detect not only hemorrhoids, but also abnormal size, shape and texture of your prostate (for men).
Anuscopy – this is a medical method of investigating your anus with a fiber optic camera called anoscope. This small tube is used for examining your anal canal and lower rectum. With this medical device, your health care provider can examine your anus in its entire length to your lower rectum.
Colonoscopy – this medical procedure is a visual examination of your colon through a colonoscope, a long, thin, flexible tube that has a tiny fiber-optic video camera and light at the end. This exam allows exploration of your rectum and the entire colon to your small intestine. With colonoscopy, your physician can detect inflamed tissue, abnormal growths, and ulcers in your intestine.
Hemorrhoids Treatment
If you have non-complicated hemorrhoids, you can treat it on your own with:
- Non-irritant laxatives
- Application of antiseptics and anesthetics (creams, ointments, pads, etc.)
- Anti-inflammatory medications intended to improve circulation and tone of veins in your anus and rectum.
Daily application of warm baths or a slice of red tomato (placing on your hemorrhoid for at least 1 hour) can also give you complete relief with non serious hemorrhoids. Both prevention and treatment of constipation should not be neglected.
In advanced forms of external hemorrhoid where there is formation of blood clot (thrombosis), surgical removal of the thrombi by a method called hemorrhoidectomy can be necessary.
Hemorrhoidectomy is a medical procedure in which the surgeon making incisions at the full height of your anus to fully remove the hemorrhoid. The wounds caused by the surgery can make the anus become sensitive. In addion, the wound requires medical care for 3 to 4 weeks. Post-surgery problems may include pain and immobilization for about 3 weeks.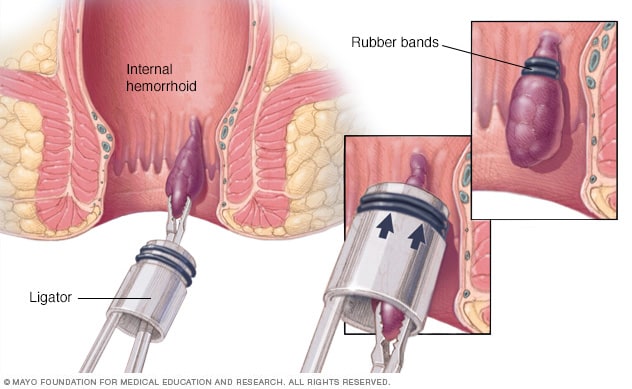
Other medical treatments can include rubber band ligation, blockage of the blood supply to the hemorrhoidal tissue by applying rubber bands to the base of the hemorrhoid; sclerotherapy, injection of a solution directly into the inflamed veins to shrink them; and stapling, a new medical procedure consisting of blocking blood flow to hemorrhoidal mass.
Anal bleeding should always be taken seriously. If youe anus bleeds immediate supervision of a health care professional is important. Anal bleeding may be the first sign of colon polyp, or colon cancer.
Hemorrhoids Prevention
- If you are obese, do your best lose weight
- Do not sit for a too long period of time
- Avoid lifting heavy objects that increases pressure in the veins of your anus or rectum
- Exercise regularly
- Prevent or treat constipation
- Increase your fiber intake
- Drink plenty of fluids – distilled water, carrot juice, lemon juice, etc.
- Eat irritant foods moderately – black pepper, coffee, alcohol, strong spices(cayenne pepper is ok)