Table of Contents
Sepsis, also called blood infections, is a serious infection of the body characterized by the presence of Pathogenic organisms (agents being able to cause human disease) in the blood. It is due to progressive discharge of bacteria in the bloodstream coming from infectious sites, skin, intestine, injuries, etc.
 At the beginning, the infection is asymptomatic. The bacteria are present in the body, but you feel do not feel any disturbing symptom. Visible signs start occurring when the immune system recognizes the intruder and reacts by releasing several substances (antimicrobial peptides) in the blood, which causes inflammation or other defensive reactions of your system. The inflammatory reaction of the body will depend on the type of (pathogenic) microorganism causing the infection: fever, Hyperventilation (rapid or deep breathing), Hypotension (low blood pressure), and more.
At the beginning, the infection is asymptomatic. The bacteria are present in the body, but you feel do not feel any disturbing symptom. Visible signs start occurring when the immune system recognizes the intruder and reacts by releasing several substances (antimicrobial peptides) in the blood, which causes inflammation or other defensive reactions of your system. The inflammatory reaction of the body will depend on the type of (pathogenic) microorganism causing the infection: fever, Hyperventilation (rapid or deep breathing), Hypotension (low blood pressure), and more.
Sepsis Causes
Any invasion in the bloodstream by virulent microorganisms can lead to cause sepsis; causes of the infection are multiple. The disease can develop due to:
- Intravenous infusion;
- Skin infection
- Gall bladder infection ;
- Respiratory infection, pneumonia for instance;
- Uterus infection following an abortion or curettage;
- Gastrointestinal infection such as Appendicitis, peritonitis;
- Surgical infection, tracheotomy for instance;
- Urinary tract infection, due to prolonged wearing of urinary catheters;
- Heart related problems including artificial heart valve, pacemaker, etc.
- Wound infection such as Infection of the skin caused by burns, wound;
- Tooth abscess or untreated dental infection, mostly in people wearing denture.
Sepsis tends to develop in hospitalized patients who are very ill. Patients at risk are mostly those with burns, artificial heart valve, aids, liver disease, kidney disorders, and diabetes mellitus. Though rare, Immunosuppressive medications, prolonged antibiotic use, and Cancer treatment can trigger the infection in patients with weekend immune system.
Sepsis Symptoms and Warning Signs
The severity of symptoms of sepsis varies from one patient to another. Nevertheless, because the disease is a life-threatening condition, you should alert a health care professional right away about any sign of the disease. Most common symptoms include:
- Confusion
- Frissons
- Skin Rashes
- low blood oxygen (Hypoxemia )
- Vomiting
- High fever
- dark gray complexion
- Cold Hands and Feet
- Falling blood pressure (hypotension)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
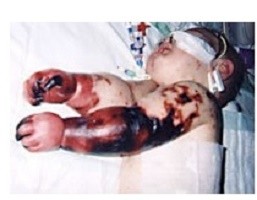
- Blood coagulation, leading to red spots on the skin (Haemorrhages into skin)
- Physical weakness (asthenia)
- Enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly).
What is the diagnosis?
The diagnosis is confirmed by Physical examination (measuring low body temperature or checking fever) and Laboratory Tests (blood culture, urine culture, CBC, platelet count, CSF culture, etc.).
Sepsis Treatment and Prevention
Your doctor would seek for the entrance door of the pathogenic agent (bacteria, viruses and fungi) and their subsequent elimination by the use of antibiotics or surgery if necessary.
Sepsis is a medical emergency that requires hospital stay. Chances of recovery depend on the number or type of organs damaged by the infection, and most importantly, your body’s response to the treatment. Earlier the infection is treated, more chance you have to survive. Any delay or negligence from either you or the doctor could have severe consequences: heart failure, kidney failure, amputation, respiratory distress syndrome (types of injuries to the lung) and even death. This disease remains the leading cause of mortality in intensive care; about 40% of Sepsis patients die.