Table of Contents
Obesity refers to an abnormal or excessive accumulation of body fat that can harm your health, according to World Health Organization (WHO).
Although obesity is more common in developed countries, it affects people around the world.
In 2005, WHO estimated that there were approximately 1.6 billion adults aged over 15 being overweight, and at least 400 million adults obese. According to the same study, by 2015, approximately 2.3 billion adults will be overweight and more than 700 million will be obese; the incidence of obesity is increasing.
In the United States only, in 2005, there were approximately 193 million people overweight and 89.8 million obese. After the USA, Mexico comes with an estimated 64.8 million overweight individuals and 25.1 million obese. That is, millions of people all over the world are overweight or obese, which puts them at risk for many serious diseases and even death.
Obesity Complications and Health Risks
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), being overweight is associated with an increased risk for:
Certain cancers – the occurrence of certain types of cancer is associated with body mass index: The list includes but not limited to bladder cancer, pancreatic cancer (cancer of the pancreas), stomach cancer, breast cancer, endometrial cancer (cancer of the endometrium), kidney cancer, esophageal cancer (cancer of the esophagus) and some types of leukemia. This risk is even higher in postmenopausal women.
Cardiovascular disease -it is shown in many studies that excessive weight gain during adolescence and early adulthood may lead to later heart disease or stroke. Therefore, to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, it is important to have a normal weight from early age.
Food addiction – obese and overweight individuals always have a tendency to have a psychological dependence on food. In addition, they often experience a feeling of depression, malaise, an unreasonable insatisfaction and emptiness between meals, which goes away when they eat.
Diabetes – Excess fat in the cells may cause insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Although the disease normally occurs from age 40, type 2 diabetes tends to develop from adolescence among people who have extra body fat; that is obese and overweight individuals.
Other diseases – other medical conditions that are linked to obesity include: Sleep apnea, hypertension, arthritis-related disabilities, dementia, caesarean section (C – section), perinatal morbidity and mortality.
If you are obese, you may also experience: osteoarthritis, gallbladder problem, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, infertility, irregular periods, infection, etc.
Economic problem – according to many surveys, the medical expenses of an obese person in the United States can be 36% higher than an individual having a normal weight.
Absence from work – according to the International Labor Organization (ILO), the problem of absenteeism is twice higher among obese workers than among healthy workers or workers having a normal weight.
Obesity Causes and Risk Factors
Obesity is often the result of an imbalance between daily energy provided by food and the sum of energy expenditure. In simple term, when you get more calories than your body burns, you increase your chance of being obese or overweight.
Your body stores a part of your intake of calories in the form of fat in the adipose tissue, a type of connective tissue that functions as the major storage site for fat in the form of triglycerides. A lack of energy expenditure can lead to an aggressive accumulation of fat, which will results eventually in overweight or obesity. However, the metabolism varies from one individual to another; some people are easier to become obese than others.
Physical inactivity – sedentary lifestyle is the main factor that can lead to an imbalance in your energy intake and total energy expenditure. In developed countries such as the United States, there is a considerable reduction in physical activities due to easy means of transport and luxury at home: remote controls, television, computers, elevators, etc.
Overeating – In developed countries, many food products with high calorie are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (24/7). The majority of these products have excessive sugar and fat. Regular consumption of these foods can lead not only to obesity but also to other serious diseases that plague our society.
Hormonal Problems – many hormonal factors such as puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause can lead to overweight. In addition, taking hormonal contraception, change in sex hormone levels and under active thyroid (hypothyroidism) can also lead to gaining a few kilos.
Medications – some psychotropic medications are sometimes responsible for being overweight; the most common include: Antipsychotics (also called neuroleptics), antidepressants, diabetes medications, antipsychotic medications, steroids and beta blockers, certain anticonvulsants and analgesics (also called pain killers).
Hereditary factors – some obese people have an abnormality in their genes responsible for the production of leptin, a key hormone in the regulation of fat reserves in the body.
Stopping smoking – especially among women, smoking cessation can lead to a few pounds in relation to the metabolic action of nicotine.
Unbalanced diet – deficiency in essential nutrients can increase your appetite, thus preventing you from having a normal weight. To be in good health and prevent obesity, it is important to eat lots of fruits and cruciferous vegetables, and reduce all foods containing: saturated fat, red meats, butter, cream, refined oils, fried chips, solid margarines, biscuits, aperitif, crackers, quiches, pies, industrial breaded products, dairy products, sugar, etc..
Obesity Signs and Symptoms
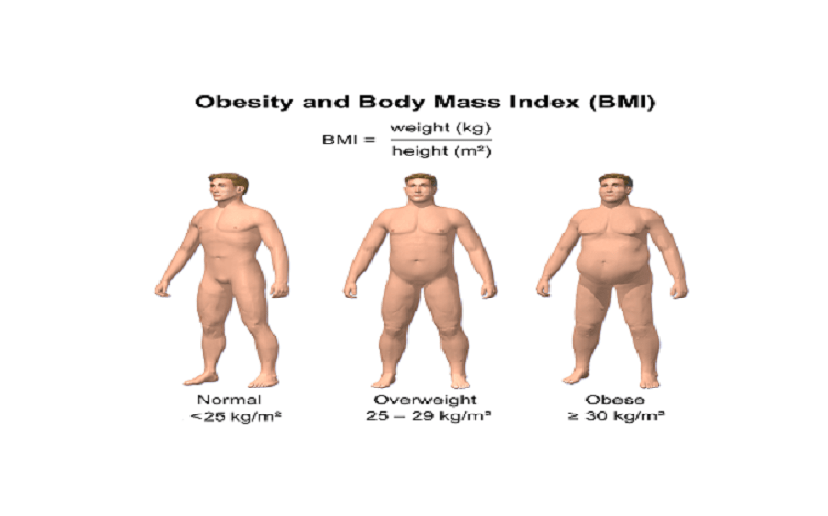
You are overweight or pbese when you have an excess of weight spreads across the board of various areas of the body. According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), being obese or overweight is having a weight that is greater than what is considered healthy for a given height. To facilitate your comprehension, refer to this exemplary table below
| Height | Weight Range | BMI | Considered |
|
5’ 9″ |
124 lbs or less | Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 125 lbs to 168 lbs | 18.5 to 24.9 | Healthy weight | |
| 169 lbs to 202 lbs | 25.0 to 29.9 | Overweight | |
| 203 lbs or more | 30 or higher | Obese |
In addition, being overweight or obese can lead to:
Social problems – it is easy to find among people who are overweight or obese a sense of self-discrimination; they tend to feel uncomfortable in public, mostly when they are among people who are in good shape.
Psychological problems – obese people often suffer from depression, ill-being, complex, inhibition, or self rejection.
In addition, if you are overweight or obese, you may also experience:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Snoring
- Daytime sleepiness
- Back or joint pain
- Excessive sweating
- Feeling hot all the time
- Skin rashes
- Infection in the folds of your skin
- Shortness of breath from even the most minor exertion.
Obesity Diagnosis
The diagnosis of obesity is mainly based on physical examination. Your doctor may ask you questions about your medical history, medication you are taking, your lifestyle: diet, exercise habit, and so on.
Physical exam – during the physical exam, the physician will examine your abdomen and measure your visceral fat (also called intra-abdominal fat), he / she may also check your blood pressure, heart rate, and sometimes your lungs functions.
Other tests – Depending on the result of the physical exam, your physician can recommend the following tests:
- Liver function tests
- Fasting glucose
- Electrocardiogram
- Hypothyroidism test
- Complete blood count (CBC).
Calculating BMI – body mass index (BMI) is the main measurement indicator used to determine your level of obesity. For adults, body mass index is equal to the weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of the size of the person (in meters): BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]2. IMC. Thus:
- Between 25 and 18.5 – normal
- Between 25 and 30 – overweight
- Over 30 – obesity
- From 35 to 40 – severe obesity
- Over 40 – morbidly obese.
Obesity Treatment (Medical)
There are drugs on the market that can help you lose wiehgt; their effectiveness, however, is often short-term, and they can cause serious side effects. They must be taken continuously; stop taking them results in regaining the weight. The result of these drugs varies from person to another; some obese people manage to lose 3 to 5 pounds for a 6 month period. Common weight loss pills include:
Sibutramine (Meridia) – Meridia, when used along with exercise, can help you lose up to 10% of your weight. It works by altering the neurotransmitters within your brain resulting in a decrease in appetite. This drugs works for some, but it may cause some side effects:
- Insomnia
- Acne
- Rash
- Dry mouth (which can lead to bad breath)
- Sinus congestion
- Constipation
- Headache and dizziness
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Nervousness
- Abdominal pain
- Chest pain
- Joint pain
- Back pain
- Muscle pain
- Neck pain
- Abnormal taste
- Abnormal menstrual periods
- Flu-like syndrome
- Persistent cough
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sore throat.
Orlistat (Xenical) – Xenical is often used in the treatment of obesity and overweight. It is an inhibitor of gastrointestinal lipases. It works by decreasing the amount of ingested fat that is absorbed systemically by preventing the hydrolysis of triglycerides. Xenical is an over-the-counter (OTC) drug; it can be bought without a prescription. Common side effects include:
- Flatulence
- Stomach pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sore throat
- Skin rash
- Flu symptoms
- Rectal pain
- Fatty/oily stools
- Fecal incontinence
- Urgent bowel movements
- Frequent bowel movements
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Oily spotting in your underwear.
Obesity Surgery
Weight loss surgery – also called bariatric surgery, weight loss surgery is a surgical method of restricting food intake in a way to decrease daily caloric intake in order to fight against obesity. It is used in most severe cases of obesity, or when the body mass index is above 40kg / m². Your bariatric surgeon may also recommend weight loss surgery in case of failure of all other attempts to help you lose weight. The three methods mostly used include:
LAP-BAND System – also called LAP-BAND surgery, this method is used to reduce the volume of your stomach so that you have a feeling of fullness quickly. During the procedure, your surgeon place around the upper wall of your stomach an inflatable ring to create a small gastric pouch; this helps to reduce the amount of food you can eat. Therefore, you will lose weight without gaining it back, since the amount of food you ingest is limited, and your digestion is slowed.
Gastric Bypass – This technique is a combination of both restrictive and malabsorptive surgery. First, the surgeon divides your stomach in two to form a small pouch at the top. The rest of the stomach and intestines are derived by stapling part of the intestine to the small gastric pouch. Therefore, after the surgery, you are unable to eat as much as before, which lead to a reduction of your absorption of nutrients and calories.
Laparotomy – also known as coeliotomy, laparotomy is a gastric restriction consisting of the creation of a bypass system in your digestive tract to decrease absorption of nutrients by your intestine. These methods can help you lose up to 40% of your initial weight, but they are often accompanied by side effects:
[row][double_paragraph]
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Infection
- Pneumonia
- Blood clots
- Gallstones
- Hernia
- Malnutrition
- Vitamin deficiencies.
Obesity Treatment (Alternative)
To lose weight, most people just go on diets. They are ready to try any weight loss product without investigating the causes of their overweight problems. It is therefore not surprising that they lose weight (just a few pounds) to gain more later. Your obesity/overweight problem is a result of many factors: lifestyle, environment, family history and genetics, or metabolism behavior.
 Regular exercise – For most people, physical activity without caloric restriction, allows them to reduce their weight. When it is associated with dieting, the result is even more satisfactisfying. However, the exercise must be done regularly over a prolonged period of time to ensure continued or long term loss of weight. You do not need to raise heavy weight to exercise; rapid walking or running is enough to give you all the benefits of an active living.
Regular exercise – For most people, physical activity without caloric restriction, allows them to reduce their weight. When it is associated with dieting, the result is even more satisfactisfying. However, the exercise must be done regularly over a prolonged period of time to ensure continued or long term loss of weight. You do not need to raise heavy weight to exercise; rapid walking or running is enough to give you all the benefits of an active living.
Dietary treatment – it is important to associate treatment of obesity a hypocaloric diet, including enough protein intake to avoid melting of lean body mass. The caloric restriction must be balanced and moderated. For example, you can reduce a quantity of 600 kcals per day compared with the usual ration. Once you gain your ideal weight, the original scheme should be gradually expanded until a return to a normal diet, while maintaining a stable weight. No matter what diet you adopt, you need to avoid saturated fats and sugary products if you really want to lose weight.
When the obesity is due to an illness, the disease must be treated or cured; otherwise, no losing weight approach will be effective. In addition, physical exercise and taking (safe) medicinal plants can be useful.
Anorectic plants – anorexic plants are all plants suppress or cause loss of appetite. Some appetite suppressor plants and medicines that seem to work for some people include: Hoodia, eucalyptus, laurel sauce, catharanthus, phyllanthus niruri, orthosiphon, algae, gum (plant) and konjac. However, a prolonged overdose of these plants increases the risk of pulmonary hypertension after years of consumption.
Depurative herbs – depurative herbs include all herbs used to purify the blood or/and organs in the body. When your liver and kidneys are working well, it is easier for you to maintain or lose weight. When used as recommended, natural depurative agents act by increasing the hepatic activity and facilitating proper disposal.
Some common depurative herbs that are being sold on the market include: dandelion, artichoke, rosemary, st Mary thistle (Silybum marianum), turmeric, and hercampuri (gentianella).
Herbal Sugar Substitutes – today, there a variety of sweet herbs that used as sugar substitute that do not have calories; in other words, they do not affect your weight: stevia, rubus suavissimus, and burl are some of them.
Obesity Prevention
Useful Tips that can help you have a normal weight. They can not only help you prevent from becoming overweight or obese but also treat it:
- Limit the time you spend being physically inactive
- Exercice regularly
- Avoid stess
- Reduce or eliminate saturated fats in your diet
- Eat a healthful diet – Eat fast foods occasionally if you cannot stop eating them
- Control your eating behavior – your need for sweet for instance
- Have adequate healthy nutriona supplements
- Rebalance your nutrients intake to enable your hormones to be more effective, particularly during menopause
- Detect and treat all thyroid disorders – under active thyroid for instance.

1 – Obésité et surpoids, WHO http://www.who.int
2 – Alimentation décente au travail: gains de productivité et amélioration du bien-être des travailleurs ; Organisation internationale du Travail (OIT)
3 – Cout économique ; wikipedia
4 – La Tribune, 17 septembre 2008, page 31
5 – Defining Overweight and Obesity: Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity and Obesity, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
6 – Albright, A.L. and Stern, J.S. (1998). Adipose tissue. In: Encyclopedia of Sports Medicine and Science, T.D.Fahey (Editor). Internet Society for Sport Science: http://sportsci.org. 30 May 1998.
7 – Initial studies in humans with the novel gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor Ro 18-0647 (tetrahydrolipstatin): JB Hauptman, FS Jeunet and D Hartmann Hoffmann-La Roche Inc, Nutley, NJ 07110-1199.