Table of Contents
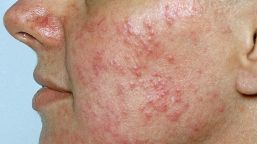
 Rosacea, also called acne rosacea, is a chronic disease of the skin characterized by the presence of persistent papules on the face. These papules are often associated with an expansion of permanent visible tiny blood vessels in the skin of the face that appear as thin red lines. Usually, the cheeks and nose are the first to take a purplish tint, followed by the forehead, chin and around the eyelids. In more advanced cases, rosacea can also be accompanied by edema, fluid collection located in the dermis and cause a slight swelling of the facial skin.
Rosacea, also called acne rosacea, is a chronic disease of the skin characterized by the presence of persistent papules on the face. These papules are often associated with an expansion of permanent visible tiny blood vessels in the skin of the face that appear as thin red lines. Usually, the cheeks and nose are the first to take a purplish tint, followed by the forehead, chin and around the eyelids. In more advanced cases, rosacea can also be accompanied by edema, fluid collection located in the dermis and cause a slight swelling of the facial skin.
Rosacea is a chronic progressive disease of vascular origin which does not lead to death; however, it can be debilitating aesthetically and even psychologically. Although rosacea can affect anyone aged 20 to 70 years, it primarily affects adults aged 30 to 50 years. Rosacea most often affects women (more than three women for one man) but men are more likely to develop a severe form called rhinophyma, a ridiculous form of acne rosacea characterized by a large, bulb-shaped, red- colored nose.
Evolution of Rosacea
The development of rosacea passes through different stages:
Early Stage: usually, the face is gradually having a reddish color, as if it was marked with sunburn. This redness is caused by a large flow of blood flowing rapidly through the skin vessels of the face. The redness of the face may be accompanied by redness and dryness of the eyes. In rare cases where the situation worsens, an inflammation of the eyelids can occur.
Intermediate Stage: without effective treatment, the redness becomes more pronounced and persistent over time. Facial skin can also become very dry. The dilation of small vessels that provide circulation to the face can occur. These vessels may become visible and create thin red lines on the skin, especially on the cheeks (telangiectasia). Small red and solid spots (papules) or pus- filled skin elevation (pustules) may appear on the face. In some patients, the eyes may be red and irritated.
Advanced Stage: at this stage, the skin inflammation becomes more deteriorated. In men (possible but rare in women), the sebaceous glands of the nose can increase in volume, forming fleshy protuberances making it seem larger (rhinophyma). In this case, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Rosacea Causes
Contrary to what is often believed, rosacea is not caused by either alcohol or unhealthy lifestyle, although they can aggravate the disease. Medically, the causes of rosacea are unknown, however there are assumptions. Rosacea can be attributed to :

- strong emotions
- prolonged exposure to sunlight
- malfunction of the connective tissue under the skin of the face
- Blood congestion (blood flow is impeded) in the front area accompanied by vascular dilation (abnormal increase in size of tiny blood vessels).
- Bacteria: acne rosacea might be resulted from helicobacter pylori. In this case, the disease is associated with inflammation of the lining of the stomach and a lack of development (atrophy) of the mucosa of the jejunum (part of the small intestine) or a lipase deficiency (an enzyme the body uses to break down fats in food so they can be absorbed in the intestine).
- Parasites: demotex folliculorum is a species of parasite of the form of worm that can be found on the surface of the skin, particularly in the sebaceous glands. The sebaceous glands are located in the epidermis, causing an oily secretion called sebum. In secreting sebum, they allow the skin to protect against external aggression and to keep certain elasticity. At the onset of rosacea, demotex folliculorum would grow excessively leading to development of papules and pustules. The causes that lead to the proliferation of demotex folliculorum are still ignored by scientists.
Rosacea Risk Factors
No one knows for sure the causes of rosacea; these factors, however, are suspected:
- alcohols and red wine
- Inadequate fluid intake – failure to drink enough water
- Hot drinks: coffee and tea have long been accused; however, scientists have found little proof. It is instead belied that hot temperature has an influence on outbreaks of rosacea
- exposure to intense cold or very hot weather
- prolonged exposure to sunlight, winds
- taking (too) hot bath
- physical effort
- Stress, anger, embarrassment, fatigue, and everything that is likely to raise blood pressure.
- Some diseases such as fever, colds, gastritis, diaphragmatic hernia or hot flashes associated with menopause.
- Some medications such as topical steroids and vasodilators, drugs that relax or dilate blood vessels.
- Skin products made of or which contain eucalyptus oil, clove oil, alcohol, witch hazel, salicylic acid, menthol or peppermint. Any product that causes skin drying or stinging, such as after –shave, can lead to rosacea outbreaks.
- Different foods are known to cause outbreaks of rosacea: spicy foods, pepper, vanilla, foods rich in histamine, vinegar, tomatoes, citrus and grapes, as swell chocolate, sour cream, yogurt, cheese, eggplant, spinach, bananas and many varieties of pulses.
Rosacea Symptoms
Initially, rosacea results in an eyes twitching and dilation of small blood vessels on the surface of the skin. It evolves in outbreaks, and its development passes through different stages (see Stages). In general, the symptoms of rosacea include:
- sensitive skin associated with a tingling in his eyes;
- Facial redness (rosacea), mainly on the cheeks but sometimes on the nose, forehead and chin;
- Appearance of small blood vessels visible on the nose and cheeks;
- Formation of small red and solid spots on the nose, cheeks, forehead and chin
- dry, red and irritated eyes
- Small pus filled bumps on the nose, cheeks, forehead and chin
- inflammation of the membrane covering the front of the eye and the inside of the eyelid ( conjunctivitis)
- The nose becomes red, swollen and covered with nodules.
Rosacea Complications
Rosacea is evolutive disease; it can cause acne flare ups, especially in times of stress or fatigue. If left untreated, it can lead to inflammation of the cheeks and eyes. When rosacea is in more advanced stage, it can severely affect vision, which requires immediate and advanced medical interventions.
Although rare, over the years, a buildup of tissue can form on and around the nose leading to serious condition called rhinophyma. Both men and women can be affected; however, rhinophyma is much more common in men.
Diagnosis
There is no specific test to diagnose rosacea. In fact, rosacea can be diagnosed by simple clinical observation. Sometimes, no laboratory testing is necessary. If complications occur, your doctor may recommend certain diagnostic procedures, depending on the characteristic of the disease.
Rosacea Treatment
Before beginning any rosacea treatment, a healthy lifestyle is necessary to be adopted. Clean your face without any aggression, with warm water and a mild non irritating soap. Wipe your face afterwards with a cotton towel without rubbing it. You can use make up, but avoid fatty or irritating skin products such as cosmetic products containing alcohol, acids, oil or/and mint. Avoid unnecessary physical effort. Also avoid stress which is a major aggravating factor of rosacea. If necessary, talk to your dermatologist or physician for more information.
It is important to avoid all factors that can worsen the symptoms of the disease such as prolonged sun exposure. The ultraviolet of the sun alters the blood vessel wall and its thermic effect trigger or worsen the symptoms of rosacea. If you must expose yourself to the sun, use sunscreen index of 20 or more. Protect yourself also from hot and cold temperature, humidity and wind. Avoid as much as possible hot drinks and foods, alcoholic beverages and hot spices.
The ultraviolet of the sun alters the blood vessel wall and its thermic effect trigger or worsen the symptoms of rosacea. If you must expose yourself to the sun, use sunscreen index of 20 or more. Protect yourself also from hot and cold temperature, humidity and wind. Avoid as much as possible hot drinks and foods, alcoholic beverages and hot spices.
Rosacea is a chronic disease; there is no curative treatment to definitively stop it. There are, nevertheless, drugs to control its evolution, and prevent its damaging effects on your face. These drugs can improve the appearance of the skin; however, it often takes several weeks to see results. The more severe the disease is the more difficult is the treatment. Therefore, it is important to consult a dermatologist quickly in the early development of the disease. Otherwise, rosacea may worsen and cause permanent damage on your face.
However, rosacea pregnancy-related needs no treatment, it usually goes away by itself a few months after childbirth. A rosacea related to facial surgery can significantly diminish with time. It is therefore advisable to wait six months after surgery before starting treatment. Rosacea that affects infants and young children may also be neglected. It disappears by itself over time as the child’s skin becomes thicker.
Drug Therapy
Antibiotics: If rosacea is caused by bacteria, antibiotic creams, especially those of the metronidazole family (antibiotic medications used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa) may be prescribed. Oral antibiotics (tetracycline and others) may be prescribed, often with success, but their prolonged use is not recommended. When skin lesions are present, doctor may prescribe topical antibiotic medications (Metrogel® and others). Those antibiotics work by killing the bacteria that contribute to inflammation.
Isotretinoin (Accutane, Sotret, Claravis, Amnesteem…): Accutane ® is sometimes used to treat rosacea. This medicine must be prescribed in cases of severe rosacea. It is important during treatment to see your doctor regularly, because Accutane is powerful drug that can cause serious side effects in some patients. In addition, Accutane is contraindicated for pregnant women or those trying to become pregnant, as it increases the risk of birth defects.
Accutane is sold under different name: Amnesteem, Claravis, Decutan, Istane, Sotret, Ratane, Raccutane, and Isotretinoin (its generic name). If you have already taken the drug, and become victim of its adverse effects, you can take legal action. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Surgical Therapy
Rosacea can leave scars in your face that requires cosmetic surgery. Some symptoms of rosacea have such as telangiectasia (small red lines caused by dilated blood vessels) and rhinophyma can require surgery to improve your appearance. Some surgeries performed in the treatment of rosacea include:
Electrocoagulation: this therapeutic procedure consists of using electrical energy to cut tissue and coagulate blood vessels. It is an effective technique; however, it may require several treatments and has various disadvantages: light bleeding, redness and the formation of small scabs-like lesions in the days that follow. In addition, there is a risk of scarring or permanent discoloration of the skin. Electrocoagulation is not recommended during the summer to prevent formation of brown spots.
Laser surgery: this laser treatment allows to devascularizing (interruption of circulation of blood to a part of your skin) an area of your skin for some years, 2-3 years most often. However, the treatment may cause some temporary bruising or reddening (making or becoming red). In addition, the therapy must be repeated regularly, and it remains relatively expensive. Nevertheless, laser surgery is more effective and less painful than the electrocoagulation; it generally leaves less scarring.
Dermabrasion: this is a surgical procedure performed to smoothen the skin and remove small scars. It consists of removing the outer layer of the skin using a small brush that rapidly rotates. After the intervention, the skin tends to be red and raw-looking; it takes several months for the skin to be normal.
Rosacea Prevention
Since the causes of rosacea are unknown, there are no precise methods to prevent its occurrence. You can, however, take steps to prevent worsening of symptoms. It is important to first identify factors that trigger or aggravate the symptoms to then learn how to manage or avoid them. In general, the following measures have enabled many people to alleviate their rosacea symptoms:
- Avoid eating foods and beverages that contribute to the dilation of blood vessels: coffee, alcohol, hot drinks, spicy foods and any food or drink that causes skin redness.
- Avoid exposure to excessive temperatures and violent winds.
- Protect your face from the cold during the winter; also avoid rapid temperature changes.
- Avoid intense exercise; it tends to trigger rosacea symptoms;
- Often relax to better manage stress and emotions.
- Avoid smoking cigarettes, because nicotine damages the vascular functions.
- Avoid saunas and extended hot baths.
- Minimize sun exposure. If you do, apply a good sunscreen 15 SPF (Sun Protection Factor) or higher against UVA and UVB in summer as in winter.
- If not recommended by your dermatologist, avoid prolonged application of coritsone creams or ointments on your face. Cortisone causes thinning of the skin, and dilated blood vessels. The wise thing to do is to read carefully the ingredients in any skin products that you intend to use. If you are not sure, talk to your dermatologist or pharmacist.