Table of Contents
Eczema is an acute or chronic allergic disease causing inflammation of your epidermis (the top layer of the skin). It is one of the most common diseases of the skin; represents about 30% of all dermatologic consultations. Unlike skin cancer, eczema is not a life threatening disease, but it can make your life miserable. Atopic dermatitis can affect anyone, but it mostly occurs in babies and children.
What are the different types of eczema?
There are many types and causes of eczema. Depending on its cause and evolution, scientists group eczema in several categories, of which the most common include:
Allergic contact eczema, commonly called contact dermatitis, this skin disorder occurs in connection with repeated exposure to allergenic substances. The most common allergens known to trigger allergic contact eczema include nickel, rubber, detergents, certain cosmetic products, and drugs. Contact dermatitis is characterized by redness of the skin (erythema), itch and sometimes, scaly desquamation. This skin disorder affects mostly adults.
Atopic eczema, also called atopic dermatitis – affects mostly atopic people, those who are hereditary predisposed to allergies. It is very usual to find children with atopic dermatitis in allergic families. Atopic eczema is characterized by redness and itch on the checks and where there is skin folding such as elbows, wrists and knees; sometimes, neck, ankles and feet. It is usually happens in the first six months of childhood, and then disappears before the age of five or before adolescence. Symptoms are triggered mainly by certain foods (milk, eggs) and environmental allergens dust, mites, pollen, etc.
Asteatotic Eczema – this type of eczema is associated with a reduction of lipids present on the surface of your skin due mainly to aging, dry climate, certain detergents, and malnutrition. It is characterized by scaly plaques dermatitis, often fissured, covering the affected area. The skin develops a pattern of superficial cracks resembling to cracking of porcelain. The disease occurs mostly in winter and among young adults or elderly who overexpose to water and detergents.
Seborrheic eczema, commonly called Seborrheic dermatitis, is a chronic form of skin disorder of unknown cause. It is characterized by inflammatory lesions more or less covered with itchy greasy scales on the scalp, eyelids, or other parts of the skin such as neck and around the nose. Seborrheic dermatitis is a very common skin condition affecting more than 3% of the US population.
Eczema Causes and Risk Factors
Cause of eczema is not well known to scientists; however, researches reveal many factors that can increase the risk of the disease. Common triggers of eczema include:
- Certain cosmetic products (Soaps, creams, etc.)
- Detergents
- Temperature changes (hot, cold, humid, or dry)
- Environmental allergens (dust, mites, pollen, etc.)
- Over exposure to water
- Food allergies (eggs, milks, peanuts, soy)
- Dry skin
- Wool and synthetic clothing
- Sweating
- Bacteria, yeasts and viruses
- Bad stress
Eczema Symptoms
In general, acute and chronic eczema may include the following symptoms:
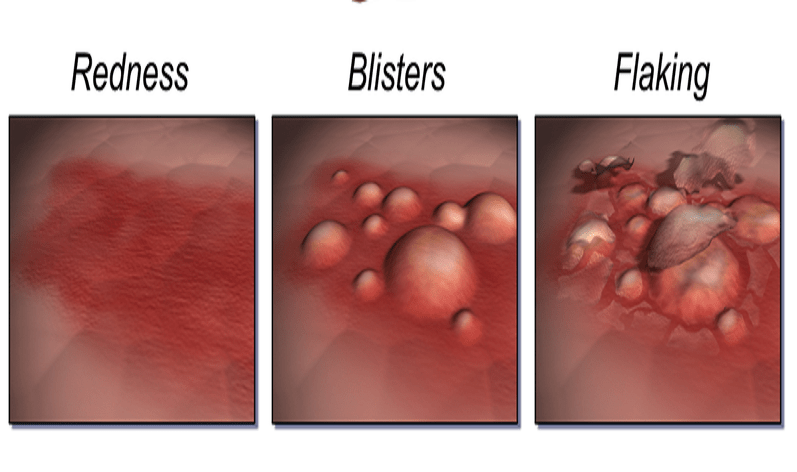
- Rash
- Ear discharge
- Pertinent itching
- Blisters with oozing and crusting
- Redness of the skin (around the blister)
- Skin inflammation (around the blister)
- skin lesions on the cheeks, elbows, knees, inside of the knees and elbows
What is the diagnosis of eczema?
Unlike most diseases which diagnosis requires many medical exams, diagnosis of eczema is, most of the times, based on the clinical symptoms and on your personal and family history. Your doctor can do a clinical examination to examine the lesions. If there is complication, your dermatologist can recommend a skin lesion biopsy to rule out other possible diseases such as skin cancer.
Eczema Treatment
 Treatment is mainly based on the cause and on the symptoms of the eczema. Therefore, contact dermatitis can disappear by avoiding contact with the allergens in question accompanied with application of cortisone or antihistamine creams. In case of atopic eczema, removal of environmental allergens as well as food allergens can sometimes bring relief. Your dermatologist can also prescribe mild anti-itch lotions or topical corticosteroids to soothe the lesions. In case of eczema caused by bacteria, yeasts or viruses, cortisone or antihistamine creams associated with antibiotics can permanently cure both the infection and the eczema. Psychological care and spa treatments are also used in the treatment of eczema. If left untreated, complication of eczema can lead to permanent scars.
Treatment is mainly based on the cause and on the symptoms of the eczema. Therefore, contact dermatitis can disappear by avoiding contact with the allergens in question accompanied with application of cortisone or antihistamine creams. In case of atopic eczema, removal of environmental allergens as well as food allergens can sometimes bring relief. Your dermatologist can also prescribe mild anti-itch lotions or topical corticosteroids to soothe the lesions. In case of eczema caused by bacteria, yeasts or viruses, cortisone or antihistamine creams associated with antibiotics can permanently cure both the infection and the eczema. Psychological care and spa treatments are also used in the treatment of eczema. If left untreated, complication of eczema can lead to permanent scars.
Eczema Diet
To get a complete relief from eczema, during the treatment you should consume a strict healthy diet.
Foods you should not eat:
Meat: all game meats, goose, duck, eel, carp, pig, salmon, shrimp, crab, mackerel, marinated meat, viscera, charcuterie (Sausages, ham, etc.), canning meat, meat extract, all crustaceans, mollusks (snails, clams, sea slugs)and all fatty meats.
Green vegetables: sorrel, asparagus, watercress, cabbage
Milk: butter and fermented cheeses
Fruits: oily fruit, peanuts, hazelnuts, walnuts, etc.
In addition, these foods are not recommanded: sugar, chocolate, pastries, fatty broth, crayfish bisque, fish soup, spices, sausages, white bread, vinegar, alcohol, aperitifs, liqueurs, beer, Wine.
Foods you should eat:
Meat: fresh partridges, chickens, rabbits, certain fresh fish (hake, dab, whiting, sole) boiled, roasted or grilled lean meats
Milk – allowed in small quantities: curdled milk, kefir, yogurt, fresh butter; non-fermented cheese is allowed in small quantities
Eggs – allowed in moderate quantities, very fresh and well cooked
Green vegetables: all vegetables except sorrel, asparagus, watercress, cabbage –
Fruits: all fresh fruits are permitted except those indicated above
Eczema Prevention
- Identify and avoid everything that aggravate or trigger the disease, sweating, wool and synthetic clothes
- Use warm water and mild soap when taking a bath
- To avoid scar, don scratch the affected area
- Avoid bad stress, anxiety and depression
- If you have dry skin, use moisturizer and drink plenty of fluids to keep your skin hydrated
- Avoid perfumes that irritate your skin
- Do not let sweat accumulates on your skin
- Do not wear clothes that prevent your skin from breathing easily
- Breast-fed your infants; breast-fed children are less apt to have eczema, according to many studies