Table of Contents
Gout is a form of arthritis resulted from elevated concentrations of uric acid in your blood stream (hyperuricemia). Those crystal deposits lead to inflammatory reaction in your connective tissues (joint, for example) and, sometimes, kidney damage.
Uric acid (urate) is a waste product found in your urine and blood. It is produced from breakdown of purine, a component of many foods such as anchovies, mackerel, liver, peas, beans, wine, herring, smelt, turkey, sweetbreads, beer, etc. At normal levels (about 0.7 g/day), urate does not repsesent any threat to your health. It becomes a problem when there are high levels in the blood.
Gout Causes
In most cases, the origin of this excess is unknown. When the origin is found, it is often linked to other metabolic diseases. That is why it is important to treat not only the “Gout”, but also the disease causing it.
The most common causes of Gout include the following:
- Lack of urinary elimination;
- Lifestyle and diet – those who consume heavily alcoholic beverages and diet rich in red meats are more at risk;
- Obesity– being overweight increases your chance to have gout
- Race – it is shown in many researches that African american and British people are more likely to develop gout;
- Sex – Although gout affects both women and men, it is more common in men; 90% of gout patients are men. In women, gout occurs mostly after menopause
- Genetic – If your parents have gout, you have higher risk of developing it;
- Excess production of uric acid from the metabolism of proteins;
- Cellular problems due to:
1) Extensive burns;
2) Hemolytic anemia;
3) Saturnism or plumbism (lead poisoning);
4) Certain treatments: corticosteroids, thiazides;
5) Kidney diseases: Kidney failure, glomerulonephritis (glomerular nephritis, GN);
6) In children: Lesch-Nyhan disease (Choreoathetosis, encephalopathy), glycogen storage disease type 1.
Gout Symptoms
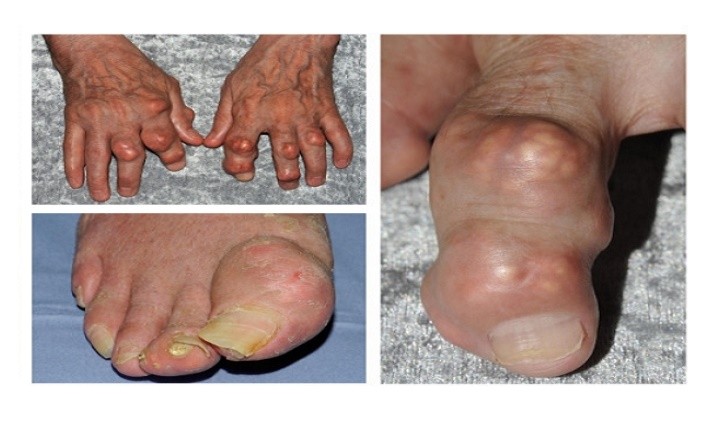
In most cases, the attacks of gout occur abruptly in the middle of the night. The pain tends to affect your big toe; however, your ankle, heel, instep, knee, wrist, elbow, fingers, and spine can also be affected. You can feel fatigue, “flu-like syndrome”, headache, etc. During the attacks, you can also have burning and inflamed joint. The areas of your joints can become red hot and very painful. In addition, you may have chronic insomnia (difficulty of falling and remaining sleep). As the disease aggravates, the pain becomes more and more atrocious. Sometimes, the pain is so severe that you cannot put your feet on the floor when you wake up. In some cases, the pain can be accompanied by a low-grade fever (ranging from 100.4°F (38°C) to 102°F (39°C)) associated with sweating and agitation.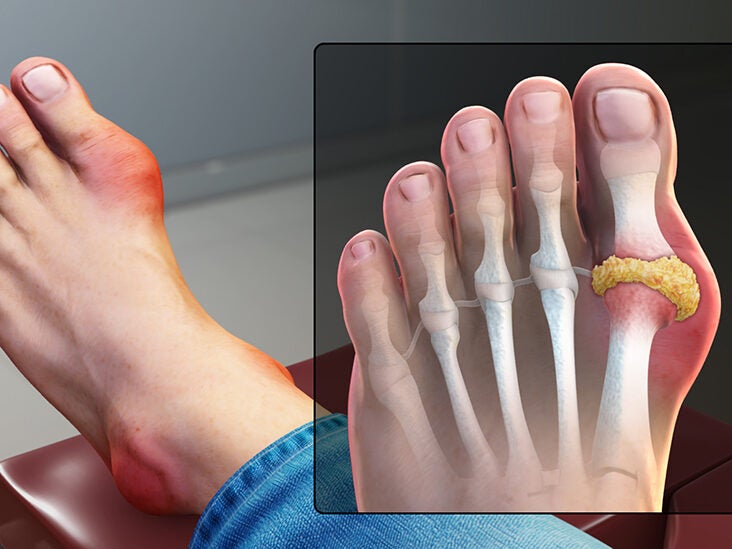
Gout Diagnosis
Gout diagnosis is based on the symptoms or damage of the disease. In some people, the evident signs are enough to conclude gout with no need for further explorations. In case there is lack of evidence, your doctor can recommend blood test to look for hyperuricemia. The blood test can be accompanied with a Joint fluid culture.
Joint fluid culture – This test is done by inserting a needle in your inflamed joint to draw a sample of synovial fluid. A specialist examines the fluid to look for infection-causing microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses). Early diagnosis is very important when it comes to gout, because gout treatments are most effective when taken in the early phase of the disease
Gout Treatment
Gout treatment is aimed at alleviating the symptoms and eradicates, if possible, the root of the disease. In addition, your doctor will try to prevent further attacks, tissue damage, and formation of kidney stones.
Medications – The medications most commonly used to treat gout are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Those drugs can relieve pain and reduce swelling and stiffness, but does not prevent damage. They may cause stomach problem: pain, bleeding, and ulcers. The discontinuity of those drugs tends to lead to the reoccurrence of the disease; long-term treatment can affect adversely the development of gout creating a form of resistance to other treatments.
Colchicine – Colchicine remains the most effective gout treatment. On average, it alleviates the symptoms in 10 to 24 hours. In most people, the drugs lead to complete disappearance of gout attacks in 3 to 4 days. However, some users complain about these following side effects:
Minor side effects:
- Hair loss
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal Cramps or Abdominal Discomfort
- Skin rash.
Major side effects:
- Numbness and tingling
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Decreased urine output
- Weakness
- Fever
- Severe sore throat
- Abnormal bleeding or bruising
- Fatigue.
Uricosuric medications – The treatment of hyperuricemia (elevated concentrations of uric acid in the blood stream) depends mainly on its origin. Uricosuric medications are the most common drugs used in the United States to reduce uric acid concentrations and prevent future concentration. People that are genetically predisposed to produce too much uric acid are treated with Allopurinol, which partially inhibits the synthesis.
Gout Complications
 Without a proper treatment, gout will affect other joints and causes serious health problems. The disease can lead to a form of gout arthropathy (destruction of hyaline cartilage with early osteoarthritis), and potentially leading to disability. The deposits of uric acid in the kidneys can lead to interstitial nephritis, renal failure or hypertension.
Without a proper treatment, gout will affect other joints and causes serious health problems. The disease can lead to a form of gout arthropathy (destruction of hyaline cartilage with early osteoarthritis), and potentially leading to disability. The deposits of uric acid in the kidneys can lead to interstitial nephritis, renal failure or hypertension.
Diet Idea
- If you are obese, try to lose weight by consuming a hypolipidic and hypocaloric diet (foods low in fat and calorie)
- Drink more than 2 liters of water per day to eliminate excess acid uric from your blood;
- Drink abundantly carrot and citrus juice (lemons, oranges)
- Eliminate or decrease the following foods in your diet: Kidney beans, mushrooms, Beef, Pork, Bacon, Lamb, duck, turkey, beer, liver, peas, alcoholic beverage, mackerel, wine, herring, smelt, and white and sweetbreads.
- Avoid shrinks , Charcuteries (Sausages, ham, cooked or processed meat foods)
- Avoid or consume moderately: Sardines, anchovies, and milt)
- Avoid or consume moderately mayonnaise, ice cream, fermented cheese, chocolate, etc.
References:
- Can Med Assoc J. 1979 April 21; 120(8): 937-41, 956.
- Journal of Applied Physiology Vol. 81, No. 6, pp. 2588-2594, December 1996 SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION AND FLUID BALANCE