Table of Contents
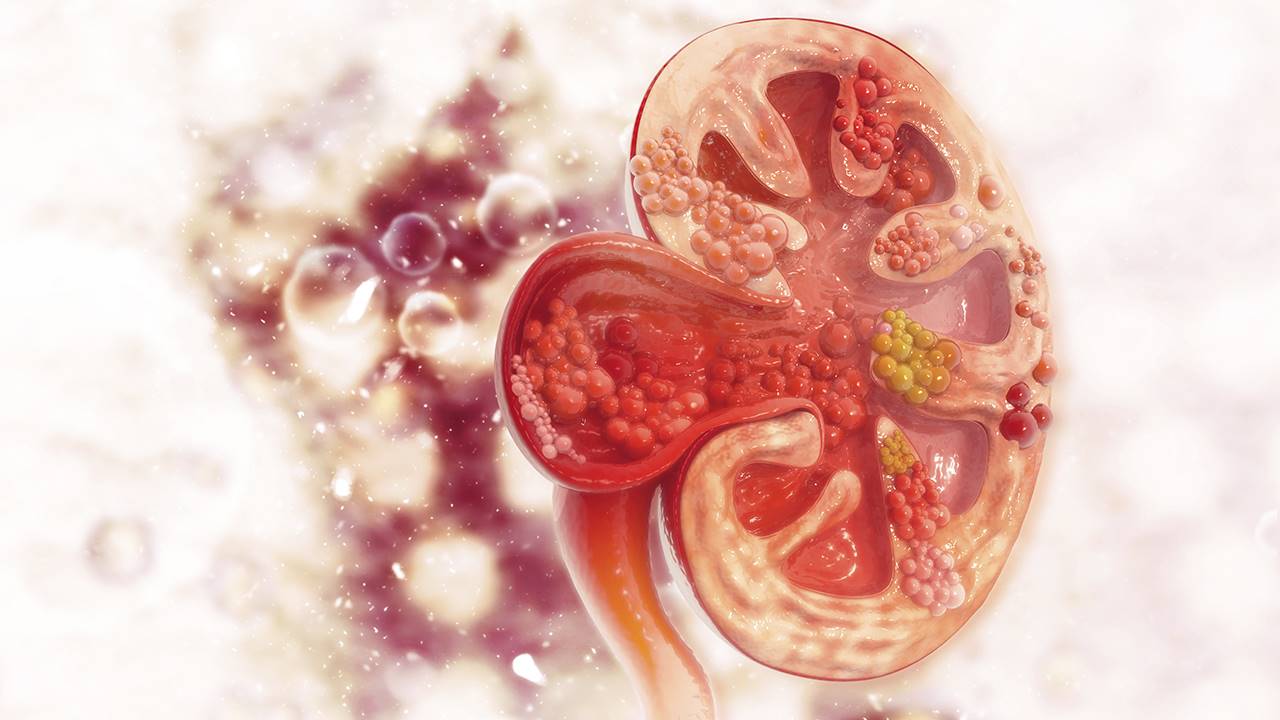
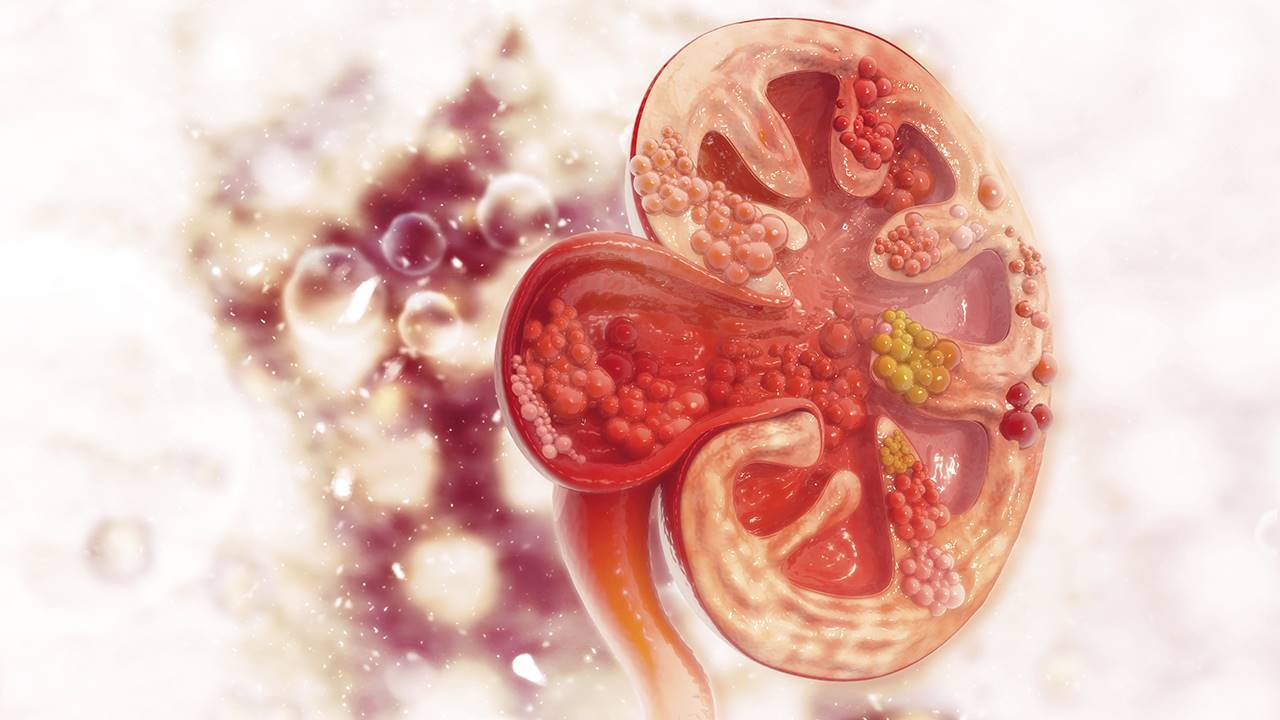
Kidney stones are formation of crystals of salts and minerals in the kidney. By urinating, your kidneys eliminate a number of wastes such as urea, uric acid, oxalate, calcium, and sodium. However, when urine is too concentrated with those substances, it becomes a saturated solution causing the development of calculi in your kidney. By sticking together, those solid deposits become large and blocked inside your kidneys. Their size varies from a grain of sand to a large golf ball; larger they are more sever the pain is.
Kidney Stone Causes and Risk Factors
80% of kidney stones are made of calcium oxalate; this is the major factor of stones formation in your kidney. Sometimes, the stones can be resulted from uric acid, a byproduct of protein metabolism. Although rare, struvite and cystine may also contribute in the development of renal calculi.
Depending of the substances forming the deposits, kidney stones are grouped in four groups:
Calcium stones – In this case, the stones are made of calcium in combination with either oxalate or phosphate. Calcium stones are the most common of renal calculi; this condition is very frequent in industrialized countries, account for more than 80% incidence of kidney stones.
Uric acid stones – less common than calcium stones, Uric acid stones are formation of crystals due to low-protein diet or high levels of uric acid in the urine. It is also suggested by some scientists that certain genetic factors can lead to the development of uric acid stones.
Struvite stones – most common in women, struvite stones are formed of struvite, a phosphate mineral. This type of renal calculi tends to be associated with presence of bacteria (Klebsiella, Serratia, providencia species) in the urinary tract that transforms urea to ammonia. Struvite stones are often large and cause severe pain.
Cystine stones – this type of renal disorder is due to excessive concentration of cystine in your urine; this is a rare form of kidney stones. Cystine stones occur when the kidneys produce abnormally excessive amounts of cystine due to hereditary disorder; it is considered as a genetic disease.
Factors contributing to formation of kidney stones include:
Lack of fluid intake – your kidneys need enough water to dilute the urine. Insufficient absorption of fluids makes it difficult for the kidneys to prevent crystallization of salts and minerals, resulting in kidney stones or other kidney damages.
Unhealthy diet – Consumption of foods that contain too much calcium oxalate and uric acid can be a problem. Foods that are rich in calcium oxalate and uric acid can promote formation of crystals in your urine; If you do not change your diet, even after treatment, new stones will be formed resulting in reoccurrence of the disease.
Family history – heredity can be a factor of kidney stones. If your parent has already had kidney stones is more likely that you develop it. However, some scientists believe that the reason is because lifestyle leading to the disease tends to be transmitted from parents to children.
Gender – Although everyone can suffer from kidney stones, men are two times more affected by the disease than women are
Diseases – certain medical conditions such as gout and inflammatory bowel disease can increase your risk of kidney stones.
Medications – certain drugs are suspected in the development of renal calculi. Some of them include furosemide (Lasix), used in the treatment of congestive heart failure, high blood pressure and edema ( hydropsy); topiramate (Topamax), an anticonvulsant drug; and indinavir (Crixivan), a protease inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS.
Kidney Stone Symptoms
The symptoms of kidney stones are unnoticed if the stones are small. It is possible to have stones in your kidney for years without suspecting it. Smaller calculus can cross the urinary tract and expelled in the urine without causing pain.
However, when large stones move into the ureter, painful kidney stone symptoms occur:
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- urinary tract infection
- Urine retention (ischuria)
- Burning or Painful sensation during urination (dysuria)
- Frequent nighttime urination (nocturia)
- Frequent daytime urination (pollakiuria)
- Discoloration of urine with a strong odor
- Presence of blood in your urine (Hematuria-)
- Presence of pus or blood in your urine (hematuria)
- Severe pain in your back, below the ribs and radiates to your genital organs and thighs. The pain may last a few minutes or hours.
How is kidney stones diagnosed?
 Before proceeding to more complicated exams, you doctor may ask you different questions about your medical and family history, medication you are taking, your lifestyle and possibly diet. He may recommend a blood test to look for excess calcium or uric acid in your blood. A urine test can be done to look for stone-forming minerals in your urine, which indicate renal calculi.
Before proceeding to more complicated exams, you doctor may ask you different questions about your medical and family history, medication you are taking, your lifestyle and possibly diet. He may recommend a blood test to look for excess calcium or uric acid in your blood. A urine test can be done to look for stone-forming minerals in your urine, which indicate renal calculi.
In addition, different exams can be performed to allow your physician to detecting the location, size and the type stones you have in your kidney. Having this information, it will be easier for him to choose a treatment best suited your condition.
Today, various procedures are available to discover presence of kidney stones:
Abdominal X-ray – this procedure help your health care provider to visualize your abdomen, and detect presence of stones in your kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder.
Computed Tomography (CT or CAT scan) – The CT scan will help your doctor to identify and evaluate disorders in your kidneys such as malformations, tumors, stones, etc.
Ultrasound – this is a noninvasive medical procedure consist of high-frequency radio waves and computer processing allowing your physician to visualize your internal organs, their size, structure and any pathological condition such as stones.
Intravenous pyelography – Intravenous pyelography is used to diagnose abnormalities in your kidneys and urinary tract. This technique allows your physician to take a series of X-rays of your kidneys and urinary tract after injecting a contrast dye into a vein.
Kidney Stone Treatment
Kidney stones are curable, but can reoccur after the treatment if you do not change the lifestyle that led to the disease: unhealthy diet, insufficient fluids intake, lack of exercise, etc.
Most small kidney stones are removed by the urinary tract without any treatment; just by drinking lots of fluids. If painful symptoms occur, it is necessary to use conventional methods to get rid of the stones.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) – this is a non-surgical medical procedure that uses shock waves to break up stones that form in your kidney, bladder, ureters, or gallbladder. The fragments are then expelled in urine during the following weeks. Many studies found that lithotripsy significantly increase the risk for diabetes and hypertension later in life; therefore avoid it if you can.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (nephrolithotripsy) – Performed for the first time in 1955 by Godwin, percutaneous nephrolithotomy is a surgical procedure done under general anesthesia. During nephrolithotripsy, the surgeon use an instrument called nephroscope to remove medium-sized or larger kidney stones through a small incision in your back.
Ureteroscopy – ureteroscopic stone removal is indicated in the treatment of ureteral stone (the stone is lodged in the ureter). This technique is very effective in the treatment of kidney stone lodged in the upper urinary tract. During the procedure, your surgeon inserts softly and gradually a small medical device called ureteroscope into your ureter to the stone. Once reached, the stone can be extracted in fragments.
After surgery, you are advised to consume a healthy diet and drink plenty of fluids to prevent formation of new stones. If, despite surgery and dietary changes there is no good result, your doctor may prescribe Thiazide Diuretic, a drug that increases urine output ; or Allopurinol, a drug used to treat gout or kidney stones by preventing the accumulation of uric acid in the organism.
Side effects of those drugs can include hypokalemia, high cholesterol, triglyceride, impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes mellitus, impotence, and more.
Kidney Stone Prevention and Diet
How kidney stones or their re-occurrence can be prevented?
To reduce the risk of developing kidney stones, follow these simple measures:
- Reduce your intakes of meat, mostly red meat
- Reduce your salt intake
- Stop or avoid refined sugars
- Dilute your urine by drinking plenty of fluids daily
- Avoid foods rich in oxalate, sorrel, spinach, rhubarb
- Identify the causes contributing to the formation of the stones and avoid them
- Eliminate all stones your presently have in your kidney, urinary tract, or bladder by following and completing appropriately your treatment.
Why is it so important to treat your kidney stones?
Complications of kidney stones can lead to:
- Chronic kidney failure
- Kidney damages or kidney cancer
- Formation of other kidney stones
- A decrease in the ability of the kidneys to filter
- Regular use of dialysis to purify your blood
- More renal colic pain and tingling due to blockage of urine flow by stones.