Table of Contents
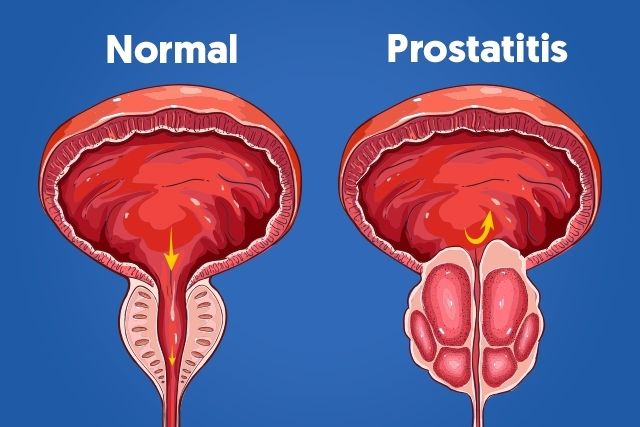
Enlarged prostate is a common medical condition among men all over the world. One of the most common causes of prostatic inflammation is Prostatitis, which is a term used to refer to a group of medical conditions causing a painful inflammation of the prostate gland.
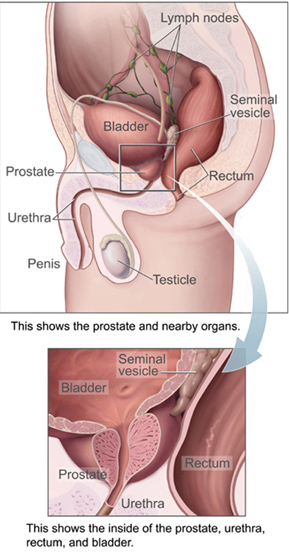
 Prostate, located beneath the bladder neck (the location where the urethra and bladder join) in front of the rectum, is the male sex gland. It is shaped like a chestnut and weighs 15 to 20 grams. It is arranged in two lateral lobes around the urethra. It has a central zone surrounding the canals ejaculation, an anterior zone and a peripheral zone, which represent 70% of the gland.
Prostate, located beneath the bladder neck (the location where the urethra and bladder join) in front of the rectum, is the male sex gland. It is shaped like a chestnut and weighs 15 to 20 grams. It is arranged in two lateral lobes around the urethra. It has a central zone surrounding the canals ejaculation, an anterior zone and a peripheral zone, which represent 70% of the gland.
Prostate, as the seminal vesicles and the bulbourethral glands, is one of the seminal accessory glands that produce the seminal plasma, from which the sperm is formed. Prostatic secretions contain zinc, citric acid and albumin: three substances that assure the chemical function of the ejaculate and promote the mobility of the sperm. From reproduction to complete well being of the body, the prostate plays a major role. However, despite its important role, the prostate is sometimes subject to disorders, of which prostatitis is the most common.
Prostatitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory infection of the prostate gland. It is a very common genito-urinary infection affecting people of all ages, with a particular frequency in young adults. Although any infection of the prostate gland can increase its chance of developing cancer, there is no proven relationship between prostatitis and prostate cancer; prostatitis, however, increases the levels of Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), a protein produced by the prostate gland that is often elevated in prostate cancer patients.
Prostatitis Causes
Depending on the causative factor of the inflammation, Prostatitis can be acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatic, asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis (chronic non-bacterial Prostatitis), or chronic Prostatitis / Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP / CPPS).
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis – This is an inflammation of the prostate gland caused, in 80% of cases, by a group of bacteria called E. coli (Escherichia coli). It is characterized by a sudden infectious syndrome accompanied by a fever of 40 ° C and urinary disorders.
Common risk factors that can lead to the development of prostatitis include:
- Untreated bladder infection
- Unprotected anal sex
- Biopsy of the prostate
- Endoscopic examination of the bladder
- Congenital or acquired anomaly (narrowing) of the urethra
- Adenoma of the prostate (also known as benign prostatic hypertrophy)
 Chronic bacterial prostatitis – It is a progressive swelling and irritation of the prostate due to an untreated or poorly treated acute bacterial prostatitis. Sometimes, a chronic prostatitis can be the result of the presence of micro abscesses in the prostate gland. It is very common, representing about 90% of all cases of bacterial prostatitis. Although it can affect men of any age, chronic bacterial prostatitis is more frequent among men over 30; it may be due to:
Chronic bacterial prostatitis – It is a progressive swelling and irritation of the prostate due to an untreated or poorly treated acute bacterial prostatitis. Sometimes, a chronic prostatitis can be the result of the presence of micro abscesses in the prostate gland. It is very common, representing about 90% of all cases of bacterial prostatitis. Although it can affect men of any age, chronic bacterial prostatitis is more frequent among men over 30; it may be due to:
- An untreated acute prostatitis
- Recurrent acute prostatitis
- Chronic urinary tract infection
- Inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis)
- Narrowing or inflammation of the urethra (urethritis)
- Chronic infectious lesions of the prostate.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis – this is a rare form of inflammation of the prostate gland. In this condition, there no clinical symptoms of prostatitis but detection of leukocytosis (increased white blood cells count) in the secretions or tissue of the prostate indicates the prostatitis. The abnormality is detected mostly during evaluation for other conditions. The cause of asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis is not clearly understood, but it is believed to be due to:
- Cancer
- Hemorrhage
- Viral, bacterial, fungal or parasitic infection
- Certain medications such as steroids.
Chronic Prostatitis / Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP / CPPS) – It is, without doubt, the most common prostate disease. It represents more than 80% of patients with pain and urinary symptoms with possible sexual dysfunctions. Contrary to other forms of prostatitis, CP / CPPS has no evidence of uropathogenic germs (can cause disease in the urinary tract, E. coli for instance); there is no trace of infection which makes antibiotic treatment usually ineffective. The cause is not clearly understood, but the following factors are suspected in the development of chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome:
- Urinary infection
- Traumatic injury (occurs mostly when lifting heavy objects)
- Age – commonly affects men older than 50 years
- Untreated stress
- Immune system disorder
- Nervous system disorder
The following factors are suspected in increasing risk of developing prostatitis:
- HIV infection
- Diabetes mellitus
- Urethra or bladder infection
- Bladder outlet obstruction
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Anal sexual intercourse
- Suppressed immune system
- Use of a urinary catheter
- Dehydration or Inadequate fluid intake
- Pelvic muscle spam
- Lifting heavy objects
Prostatitis Symptoms and Signs
In general, symptomatic prostatitis (acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, CP / CPPS) are brutal and accompanied by:
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in the urine
- Dysuria (difficulty urinating)
- Burning during urination
- Lumbar pain, lower back or groin
- Decreased sexual potency (impotence)
- Pain or discomfort of the testicles or penis
- Pain in the area between the penis and rectum
- Nocturia (frequent urination at night)
- Pain in joints and muscles.
The above conditions are considered chronic and serious if they last three months or more. They should not be neglected to avoid serious complications:
- Pelvic pain
- Painful ejaculation
- Chronic urinary tract infection
- Abscess in the prostate gland
- Unreasonable lack of sexual desire
- Urine retention or painful urination
- Orchiepididymitis (inflammation of the testis and epididymis)
- Bacteremia (Bacterial infection of the blood).
Prostatitis Diagnosis
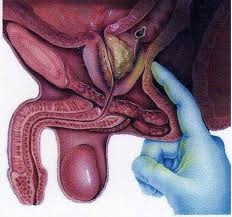 The first step your doctor will take to examine your prostate is a digital rectal examination (DRE). During the exam, your physician will use a gloved, lubricated finger to check for abnormalities in your prostate gland: enlarged prostate, swelling and tenderness of the scrotum, etc. However, the digital rectal exam is not enough to confirm the diagnosis; other tests such as urine and semen test, vesicoprostatic ultrasound, cystoscopy and biopsy of the prostate will be performed to accurately diagnose the prostatitis.
The first step your doctor will take to examine your prostate is a digital rectal examination (DRE). During the exam, your physician will use a gloved, lubricated finger to check for abnormalities in your prostate gland: enlarged prostate, swelling and tenderness of the scrotum, etc. However, the digital rectal exam is not enough to confirm the diagnosis; other tests such as urine and semen test, vesicoprostatic ultrasound, cystoscopy and biopsy of the prostate will be performed to accurately diagnose the prostatitis.
Digital rectal exam (DRE) – during this proctologic exam, your doctor introduces a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum through the anus to detect any sign that indicates prostatitis. In case of prostatitis, the prostate is enlarged and painful. Although painless, this exam, however, can be uncomfortable for some patients. DRE can only reveal if the prostate is tender or inflamed; it cannot determine the causative factor of the disorder.
Urine and semen test – to do this test, a lab specialist will take sample of your urine and semen to look for bacteria and white blood cells. This exam will detect the germs responsible for the infection, and pus in the urine if there is any. The prostatitis is most often caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in patients under 35 years, and Escherichia coli (E.coli) in older patients.
Vesicoprostatic ultrasound – this imaging technique is a noninvasive medical test that helps your physician to diagnose prostatitis and other medical conditions. It allows your health care provider to examine your bladder and prostate gland and their surrounding tissue. During the procedure, the specialist inserts an ultrasound probe into your rectum, which allows him/her to detect abnormal change in your prostate and bladder.
Cystoscopy – your doctor may recommend a cystoscopy of your urethra and bladder. Under local anaesthesia, a tube with a small camera on the end called cystoscope is inserted through your urethra and into the bladder. It allows your doctor to take picture of the inside of your bladder and urethra. Cystoscopy is performed in case of recurrent prostatitis to rule out other disorders of the prostate gland.
Prostate biopsy – to rule out prostate cancer, your doctor may recommend a biopsy of prostate. During the procedure, small samples of your prostate gland are taken to be examined under microscope to look for the presence of cancer cells. After the biopsy, for several days or even several weeks, you will tend to have:
- Bleeding in the urine
- Bleeding in the stool
- Blood in the ejaculate
Prostatitis Treatment
 If you have symptoms related to prostatitis, even before knowing the results of the exams, your doctor may recommend that you take appropriate amount of rest accompanied by antibiotherapy. Antibiotics should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor to avoid drug resistance or recurrence of the infection.
If you have symptoms related to prostatitis, even before knowing the results of the exams, your doctor may recommend that you take appropriate amount of rest accompanied by antibiotherapy. Antibiotics should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor to avoid drug resistance or recurrence of the infection.
Medication – treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis is often simple and usually last four weeks or less. Chronic prostatitis treatment, however, is often difficult and durable. In addition, in severe form of prostatitis, you may be required to be hospitalized to take the medications by injection. In case of painful urination (dysuria) or prostatitis related pain, along with antibiotics, your urologists can recommend you to take: anti inflammatory drugs, analgetics, alpha blockers (or adrenergic alpha-antagonists) drugs. Some of common antibiotics used to treat bacterial prostatitis include:
- Bactrim
- Ciprofloxacin
- Tetracycline
- Carbenicillin
- Erythromycin.
Surgery – transurethral resection of the prostate is rarely used in prostatitis treatment. It consists of visualizing the prostate gland through the urethra and removing abnormal tissue by dissection. This method, however, is not recommended for young people and can lead to infertility and other serious medical conditions.
Prostate massage – massage of the prostate gland is a painless procedure done with delicacy. The massage is practiced by some doctors as a treatment against chronic prostatitis and in certain other medical conditions that can cause the prostate gland to swell or inflame. It is aimed at evacuating the excess prostatic fluid and/or alleviating painful congestion of the prostate. Its effectiveness, however, is controversial.
To increase your chasnce of recovery, it is extremely important to play an active role during the treatment in living a healthy lifestyle. It is recommended, to prevent recurrence or complication, avoid spicy foods, tobacco and alcohol. Sex is not prohibited, however, it would be better not to take sexual enhancement pills or any synthetic sex booster. If you have impotence or erectile dysfunction, use natural alternative such as horny goat.
Enlarged Prostate Alternative Treatment
Certain herbal remedies are claimed to have curative effects on prostatitis. The efficacy of those remedies, however, cannot be surely determined. The good news is that most of them, taking in normal dosage, have no adverse effects; therefore, you can always try them. Some of them include:
- Increase FLAX SEED OIL in you diet
- Take Fenugreek and saw palmetto supplements
- On an empty stomach, Drink Corn husk tea 4 times a day for 3 weeks ( no sugar please)
- Take Pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, and flax seed daily (you need a grinder to pulverize them)
- Black spruce (Picea mariana) oil: Essential oil of black spruce is rich in terpenes and ester. it is often used in the treatment of inflammation of the prostate. At least twice a day, massage your lower abdomen with 2 to 3 drops 3 drops diluted in vegetable oil.
- Helichrysum italicum (also called Immortelle) – this plant has decongestive and anti-inflammatory properties; using it regularly can give you a noticeable relief from prostatitis. Morning and evening for 20 days, apply 2 drops of pure Helichrysum Italicum on your groin and massage the area gently. Stop for 7 days, and then repeat for 3 months. Stop the application for 7 days every 20 days until complete relief.