Table of Contents
Autism is a complex developmental disorder affecting the brain function, making it difficult or even impossible for the autistic to establish social interaction with the world environing. In addition, people with autism can often suffer from learning difficulties
The term “autism” was coined in 1910-1911 by the Swiss psychiatrist Eugene Bleuler. Back then, It was a very rare disease affecting 2 to 4 children per about 10 000. Today, the number increases. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 1 in 150 children in the United State of America is autistic.
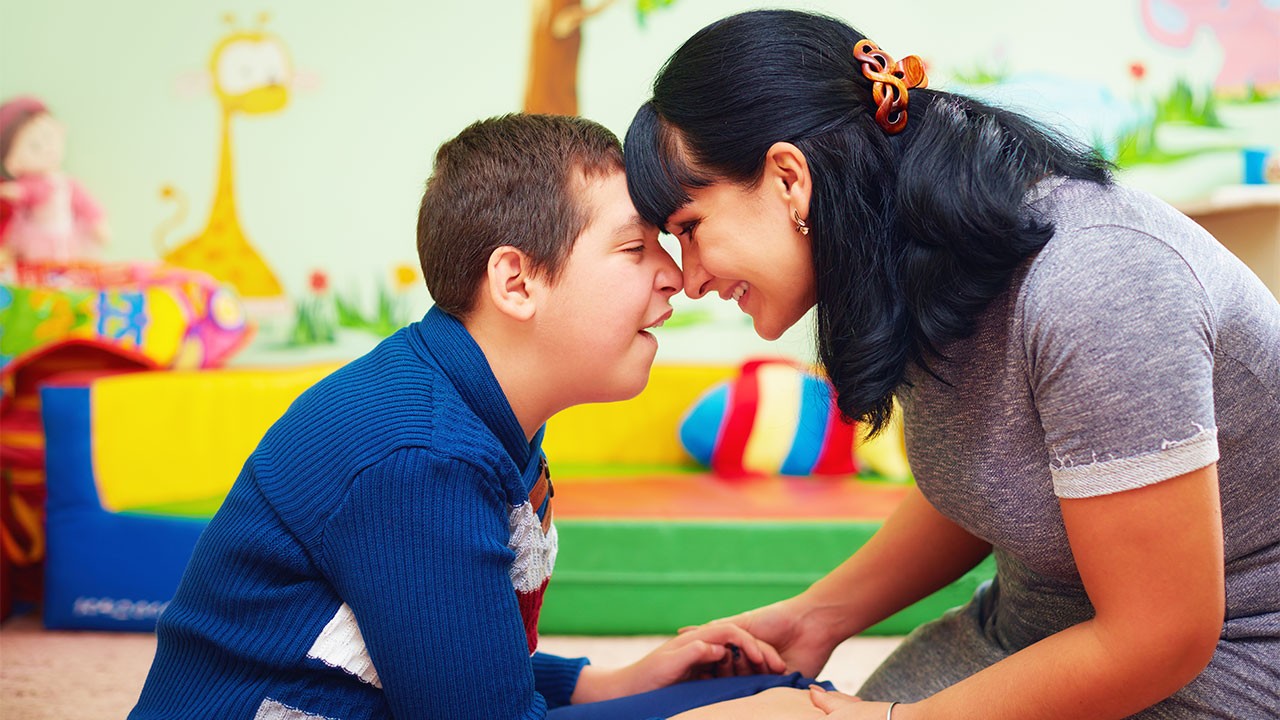
The disease occurs in all racial and ethnic groups; however, it seems more widespread among high social classes. While it affects both sexes, it is three to four times more likely to affect boys than girls. The disorder is undoubtedly present from birth, but it visibly occurs (visible symptoms) around the age of 3. The symptoms and severity of the disease vary widely from one child to another.
Autism Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of autism remain unknown to science. Scientists only speculate theories. According to those theories, the causes may be genetic, viruses, immune system disorder, diet, chromosomal abnormalities and toxins or pollutants.
Genetic – genetic causes in the development of autism are not yet evident. However, recent advanced studies show that genetic factors may be linked to the disease.
Researchers have identified two genes associated with autism in certain regions of the brain of autistic patients. Located on chromosome X, the two genes are Neuroligin 3 (NLGN3) and Neuroligin 4 (NLGN4). Scientists suggest that mutations in these genes may be associated with abnormal serotonin levels and other neurotransmitter disorders in the brain. These genes are not the sole and unique genes for autism but these studies, nevertheless, open up new doors of research to better understand the causes of the disease, and possibly find the treatment.
Toxins – presence of Toxins and certain chemicals in the organism can trigger autism. Those toxins may be originated from MMR vaccine (vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella), certain food ingredients and disruption in the immune system. However, many often refute these theories
Viruses – It is suggested that some viruses, which are known to be harmful to the brains of babies, play a role in the onset of autism. Some of the Viruses suspected include cytomegalovirus (CMV), Herpes simplex virus, rubella virus and perhaps the influenza virus.
Heavy metals – Heavy metals such as mercury, lead, cadmium are harmful to the brain, and could be a cause of autism. In some older vaccines, thimerosal (an organo-mercury preservative used in vaccines since the 1930’s) was used, which could increase the risk of autism. However, this assumption should be analyzed in more children before being accepted for fact. Like the other theories, this one raises more questions than answers. However, it is certainly safer to administer vaccines without mercury or thimerosal-free.
Poor diet – the fact that scientists notice a deficiency of fatty acids (such as omega 3), minerals and essential metals (zinc or magnesium), they theorize this deficiency could be trigger of autism. Again, no obvious link between these nutrients and the onset of autism has been fully demonstrated.
Immunity – abnormalities in the immune system are regularly detected among children with autism. The connection between the immune system and brain development is particularly complex. Currently, there is no evidence about the fact that a disorder of the immune system directly influences brain development of young children to cause autism.
Autism Signs and Symptoms
Autism is a disorder that affects people by impairing communication and social interaction with those around them. Autistics have difficulty establishing significant relationships with others. Their ability to develop friendships is generally limited as is their ability to understand the emotional expression of others.
In general, autism is characterized by a disorder of social behavior with a lack of reaction to emotions and adaptation. There are also a communion alteration with a repetitive verbal language and stereotype. In severe cases, seizures and repetitive behaviors with self and aggression can be observed.
Children with autism often have fears and phobias, unjustified fears of a situation, an object, or taking any action. Sleep disorder can occur frequently. The intelligence quotient (IQ) is very variable in autistic children. In more than 5% cases, there is a significant mental retardation. However, in sperger syndrome, a form of autism, the autistic may have good verbal expression and sometimes have extraordinary capacities in music, mathematics or painting.
What is the diagnosis of autism?
 As autism is a complex disorder characterized by a wide variety of symptoms of varying severity, it is often difficult to establish a diagnosis. However, earlier the diagnosis is established, better the chance to receive assistance and support. Medical Examinations of autism depend on the symptoms and age of the autistic. It is possible to detect early signs of autism in young children, even if they are only 18 months old. Contact a medical specialist immediately for any signs of autism that you suspect in your child.
As autism is a complex disorder characterized by a wide variety of symptoms of varying severity, it is often difficult to establish a diagnosis. However, earlier the diagnosis is established, better the chance to receive assistance and support. Medical Examinations of autism depend on the symptoms and age of the autistic. It is possible to detect early signs of autism in young children, even if they are only 18 months old. Contact a medical specialist immediately for any signs of autism that you suspect in your child.
Before declaring autism, your doctor will make very specific analyses that can help him to rule out other mental health problems or genetic disorders having symptoms similar to those of autism: Landau-Keffler Syndrome, phenylketonuria, tuberous sclerosis and Martin-Bell syndrome or Fragile X syndrome.
Autism Treatment
There is no cure for autism. Nevertheless, some methods (therapies) are used to treat children and adults with autism. The treatment must be done individually (taking medications for instance) and in groups by institutions and multidisciplinary team (socio-educative group, Foster homes, etc.).
Psychotherapies are also used in treating children and adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This includes environmental/Educational therapies. In this method the autistic are taught to respond appropriately to social and environmental stimulation: Behavior therapies aimed at reducing behavior problems and improve adaptation skills; and communication therapies, a group of methods used to help autism patients to develop useful and appropriate communication skills.
Drug therapies – Medications mostly used in autism treatment are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI’s): fluvoxamine (Luvox), for age 8 and older; sertraline (Zoloft), for age 6 and older; and clomipramine (Anafranil), age 10 and older. Like all drugs, those medications have adverse effects, which may include: nausea, depression and anxiety, drowsiness, headache, clenching of teeth, dizziness, loss of appetite, weight loss/gain, liver or kidney damage, etc.
For seizure, your doctor may prescribe anticonvulsants: (Tegretol), lamotrigine (Lamictal), topiramate (Topamax), and valproic acid (Depakote).
Healthy Diet – diets rich in of fatty acids (especially the omega-3 fatty acid DHA), minerals (zinc, magnesium) show positive results in autism patients. Increasing those supplements in your autistic children diet is vital.
Chelation therapy – The fact that heavy metals can trigger the disease, Chelation therapy is sometimes used as an alternative treatment of autism. Chelation therapy is suggested by some doctors hoping it will remove mercury from the body. However, no studies have shown a link between mercury and autism, and no one can be sure if chelation therapy really works.



